- Home
- rdx s1
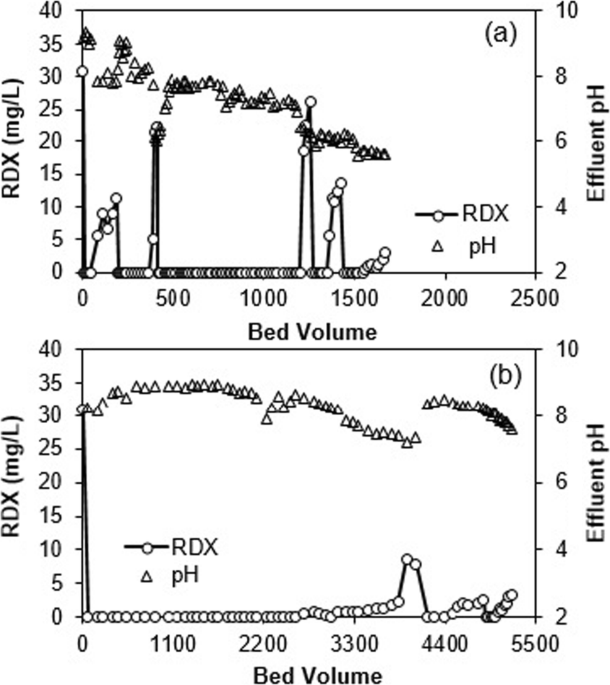
- Hexahydro-1,3,5-trinitro-1,3,5-triazine (RDX) reduction by granular zero-valent iron in continuous flow reactor
Hexahydro-1,3,5-trinitro-1,3,5-triazine (RDX) reduction by granular zero-valent iron in continuous flow reactor
4.6 (144) · $ 20.99 · In stock

Assessment of aged biodegradable polymer‐coated nano‐zero‐valent iron for degradation of hexahydro‐1,3,5‐trinitro‐1,3,5‐triazine (RDX) - Xiao - 2013 - Journal of Chemical Technology & Biotechnology - Wiley Online Library

PDF) Kinetics of RDX degradation by zero-valent iron (ZVI
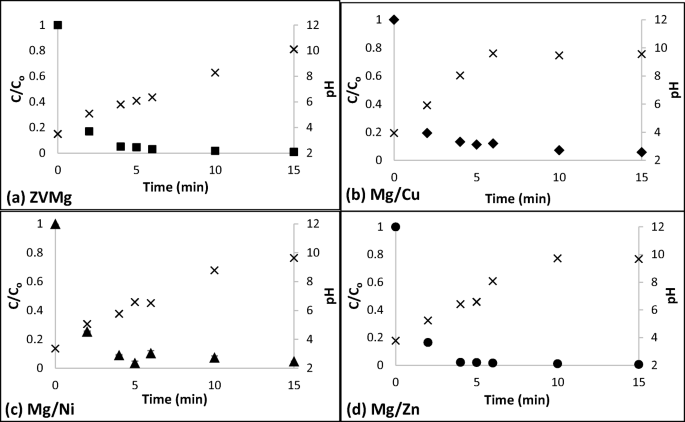
Kinetics of Reductive Degradation of 2,4-dinitroanisole (DNAN) Using Mg-Based Bimetals

Chemical structures of NTO (1) and DNAN (2)

Bacterial degradation of hexahydro-1,3,5-trinitro-1,3,5-triazine (RDX)

Characteristics of RDX degradation and the mechanism of the RDX exposure response in a Klebsiella sp. strain - ScienceDirect

Biogeochemical Dynamics in Zero-Valent Iron Columns: Implications for Permeable Reactive Barriers

Preparation, High-Density Spherical, and Low Sensitivity of RDX/NC/PMMA Composite Particles

Kinetics of Reductive Degradation of 2,4-dinitroanisole (DNAN) Using Mg-Based Bimetals

A kinetic model for cathodic degradation of explosives in a flow-through electrochemical reactor - ScienceDirect

Kinetics of Reductive Degradation of 2,4-dinitroanisole (DNAN) Using Mg-Based Bimetals

Anaerobic treatment of low-strength synthetic TCF effluents and biomass adhesion in fixed-bed systems

Production of Submicrometer-Sized Hexahydro-1,3,5-trinitro-1,3,5-triazine by Drowning-Out

The Fate of the Cyclic Nitramine Explosive RDX in Natural Soil

PDF) Hexahydro-1,3,5-trinitro-1,3,5-triazine (RDX) reduction by granular zero-valent iron in continuous flow reactor