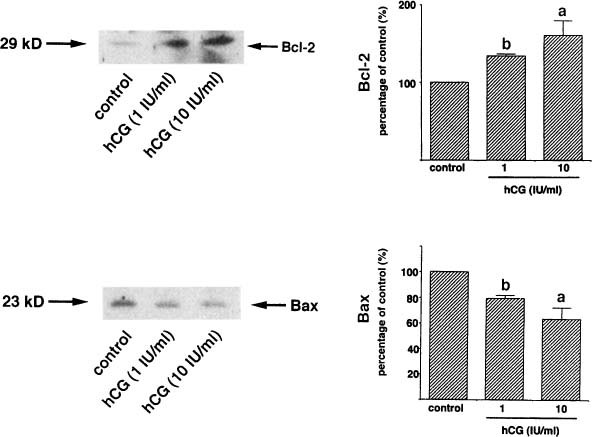
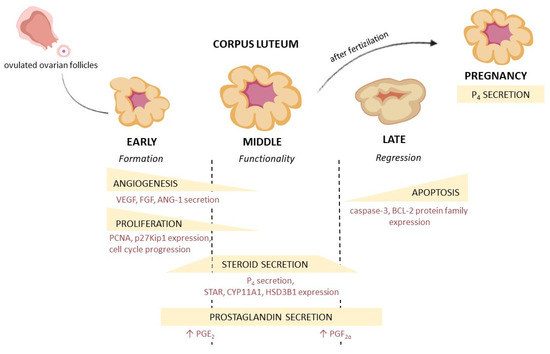
The corpus luteum is a small gland of great importance because its proper functioning determines not only the appropriate course of the estrous/menstrual cycle and embryo implantation, but also the subsequent maintenance of pregnancy. Among the well-known regulators of luteal tissue functions, increasing attention is focused on the role of neuropeptides and adipose tissue hormones—adipokines. Growing evidence points to the expression of these factors in the corpus luteum of women and different animal species, and their involvement in corpus luteum formation, endocrine function, angiogenesis, cells proliferation, apoptosis, and finally, regression. In the present review, we summarize the current knowledge about the expression and role of adipokines, such as adiponectin, leptin, apelin, vaspin, visfatin, chemerin, and neuropeptides like ghrelin, orexins, kisspeptin, and phoenixin in the physiological regulation of the corpus luteum function, as well as their potential involvement in pathologies affecting the luteal cells that disrupt the estrous cycle.
Cells, Free Full-Text
Nutrients, Free Full-Text
Cells, Free Full-Text

New Dead Cells Update Brings a Flood of Free Content from Classic

How cell-free systems work and when you should use them

ECMatrix™ Laminin Substrates are Superior Xeno-free Extracellular
Cells, Free Full-Text, spider silk tibia
Cells, Free Full-Text

Cells, Free Full-Text

Cells An Open Access Journal from MDPI

Cell-Free Assays
FreeCell Rules
Cells, Free Full-Text, freecell online 100

Cells, Free Full-Text

Cellular Respiration








:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Health-The-four-stages-of-the-menstrual-cycle-Horiz-1258de656aa9460d819fb0724fd226d7.jpg)