- Home
- high intensity
- Frontiers Elevated Lactate by High-Intensity Interval Training Regulates the Hippocampal BDNF Expression and the Mitochondrial Quality Control System
Frontiers Elevated Lactate by High-Intensity Interval Training Regulates the Hippocampal BDNF Expression and the Mitochondrial Quality Control System
4.7 (192) · $ 17.00 · In stock

Figure 3 from Acute exercise increases brain region-specific expression of MCT1, MCT2, MCT4, GLUT1, and COX IV proteins.

Lactate Mediates High-Intensity Interval Training—Induced Promotion of Hippocampal Mitochondrial Function through the GPR81-ERK1/2 Pathway

Exogenous lactate augments exercise-induced improvement in memory but not in hippocampal neurogenesis
Frontiers Elevated Lactate by High-Intensity Interval Training Regulates the Hippocampal BDNF Expression and the Mitochondrial Quality Control System
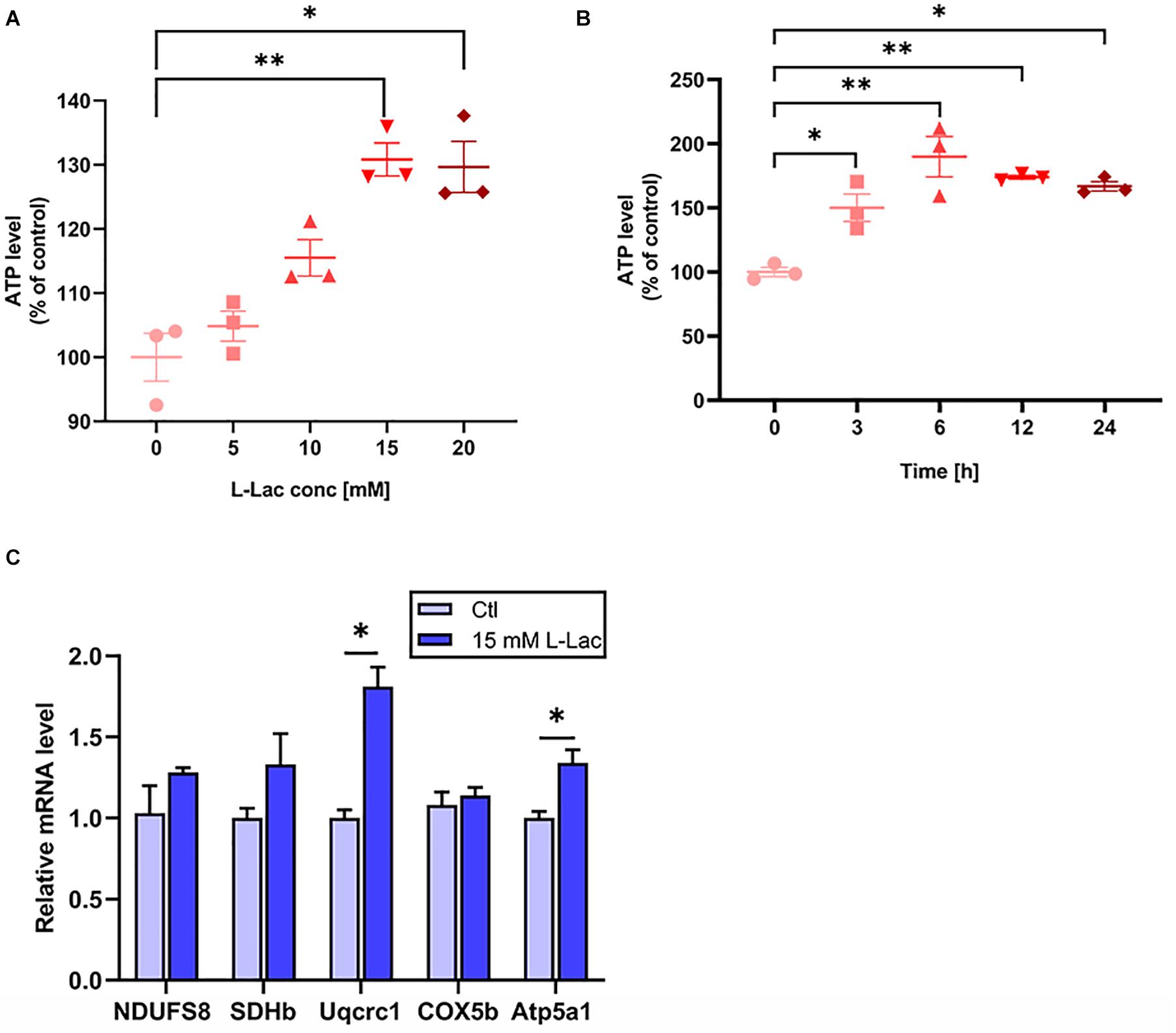
Frontiers Exogenous L-lactate administration in rat hippocampus increases expression of key regulators of mitochondrial biogenesis and antioxidant defense
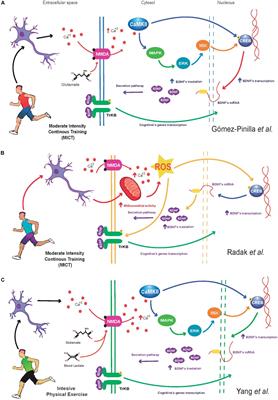
Frontiers The Impact of High-Intensity Interval Training on Brain Derived Neurotrophic Factor in Brain: A Mini-Review

Physiological significance of elevated levels of lactate by exercise training in the brain and body - ScienceDirect

Lactate Is Answerable for Brain Function and Treating Brain Diseases: Energy Substrates and Signal Molecule. - Abstract - Europe PMC
PDF) Lactate as Potential Mediators for Exercise-Induced Positive Effects on Neuroplasticity and Cerebrovascular Plasticity

The effects of long-term lactate and high-intensity interval training (HIIT) on brain neuroplasticity of aged mice - ScienceDirect

Exogenous lactate augments exercise-induced improvement in memory but not in hippocampal neurogenesis
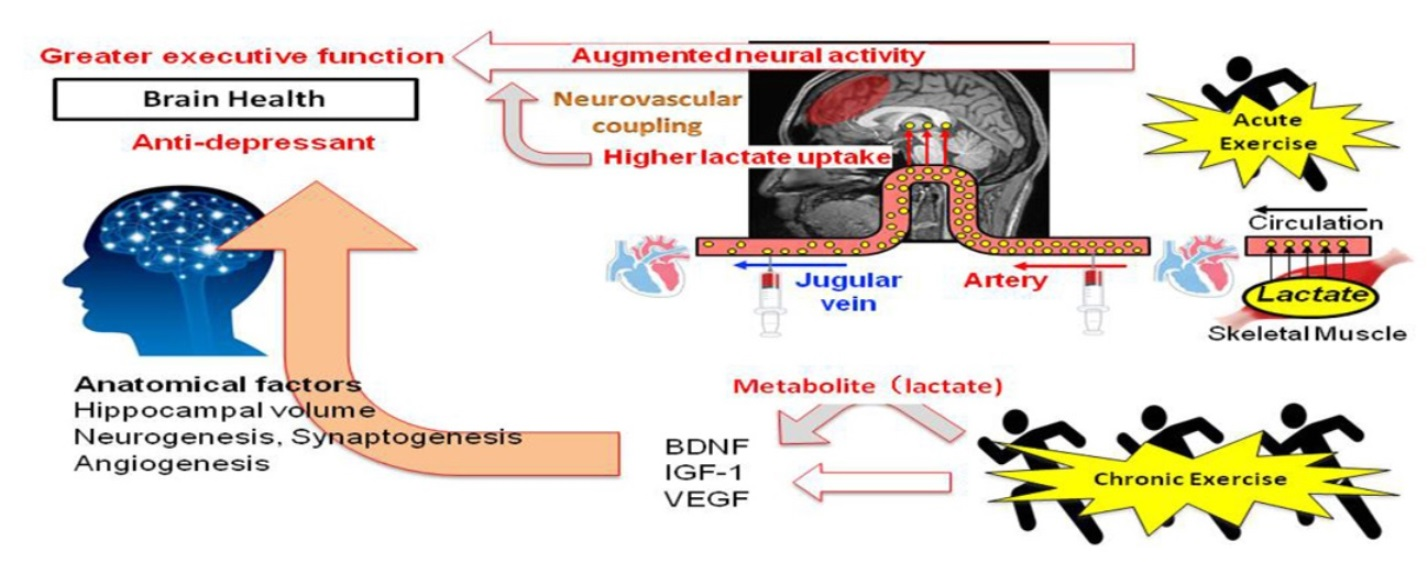
Metabolites, Free Full-Text

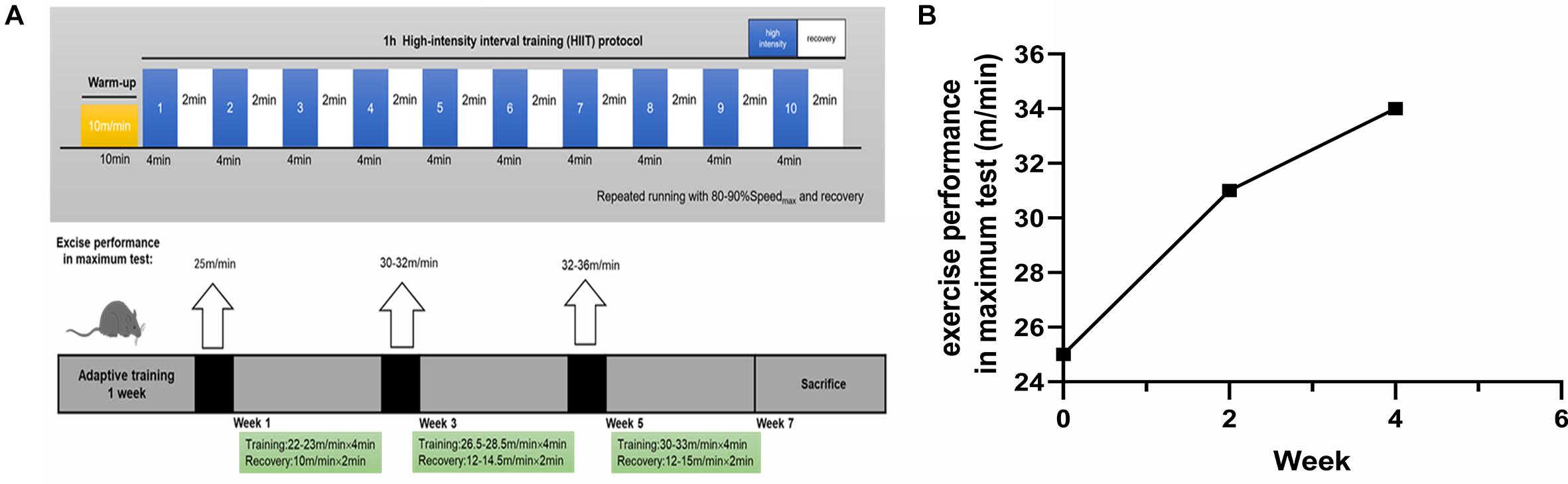
Mechanism proposed about the High Intensity Interval Training (HIIT)