Micromachines, Free Full-Text
4.9 (546) · $ 21.00 · In stock
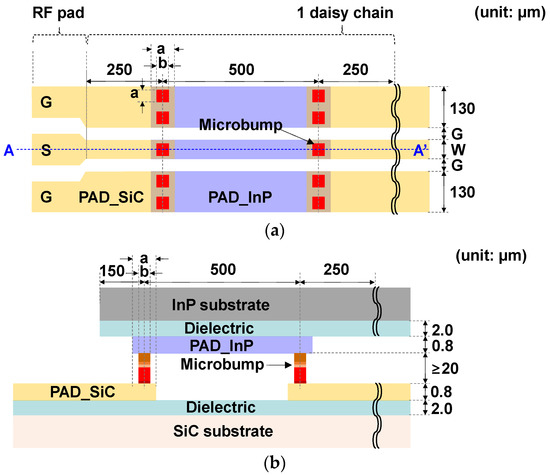
Flip-chip microbump (μ-bump) bonding technology between indium phosphide (InP) and silicon carbide (SiC) substrates for a millimeter-wave (mmW) wireless communication application is demonstrated. The proposed process of flip-chip μ-bump bonding to achieve high-yield performance utilizes a SiO2-based dielectric passivation process, a sputtering-based pad metallization process, an electroplating (EP) bump process enabling a flat-top μ-bump shape, a dicing process without the peeling of the dielectric layer, and a SnAg-to-Au solder bonding process. By using the bonding process, 10 mm long InP-to-SiC coplanar waveguide (CPW) lines with 10 daisy chains interconnected with a hundred μ-bumps are fabricated. All twelve InP-to-SiC CPW lines placed on two samples, one of which has an area of approximately 11 × 10 mm2, show uniform performance with insertion loss deviation within ±10% along with an average insertion loss of 0.25 dB/mm, while achieving return losses of more than 15 dB at a frequency of 30 GHz, which are comparable to insertion loss values of previously reported conventional CPW lines. In addition, an InP-to-SiC resonant tunneling diode device is fabricated for the first time and its DC and RF characteristics are investigated.

Micro but Many – Micro Machines' history and influence
Micro Machines, Nintendo
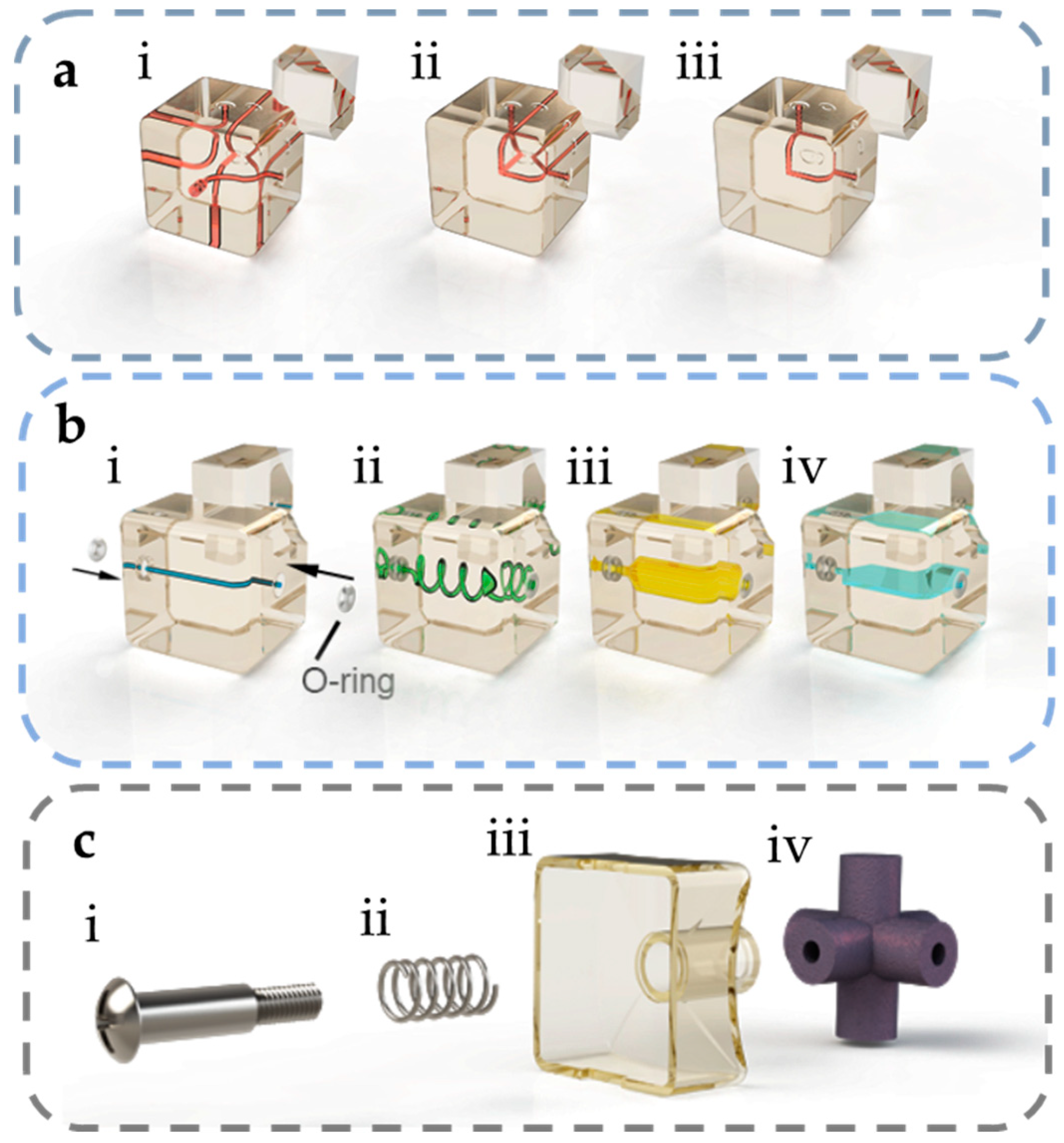
Overview of Rubik's Cube and Reflections on Its Application in

Transparency Film for Inkjet Printers 30 Sheets Qatar

Micro Machines will be revived by toymaker Hasbro: small cars
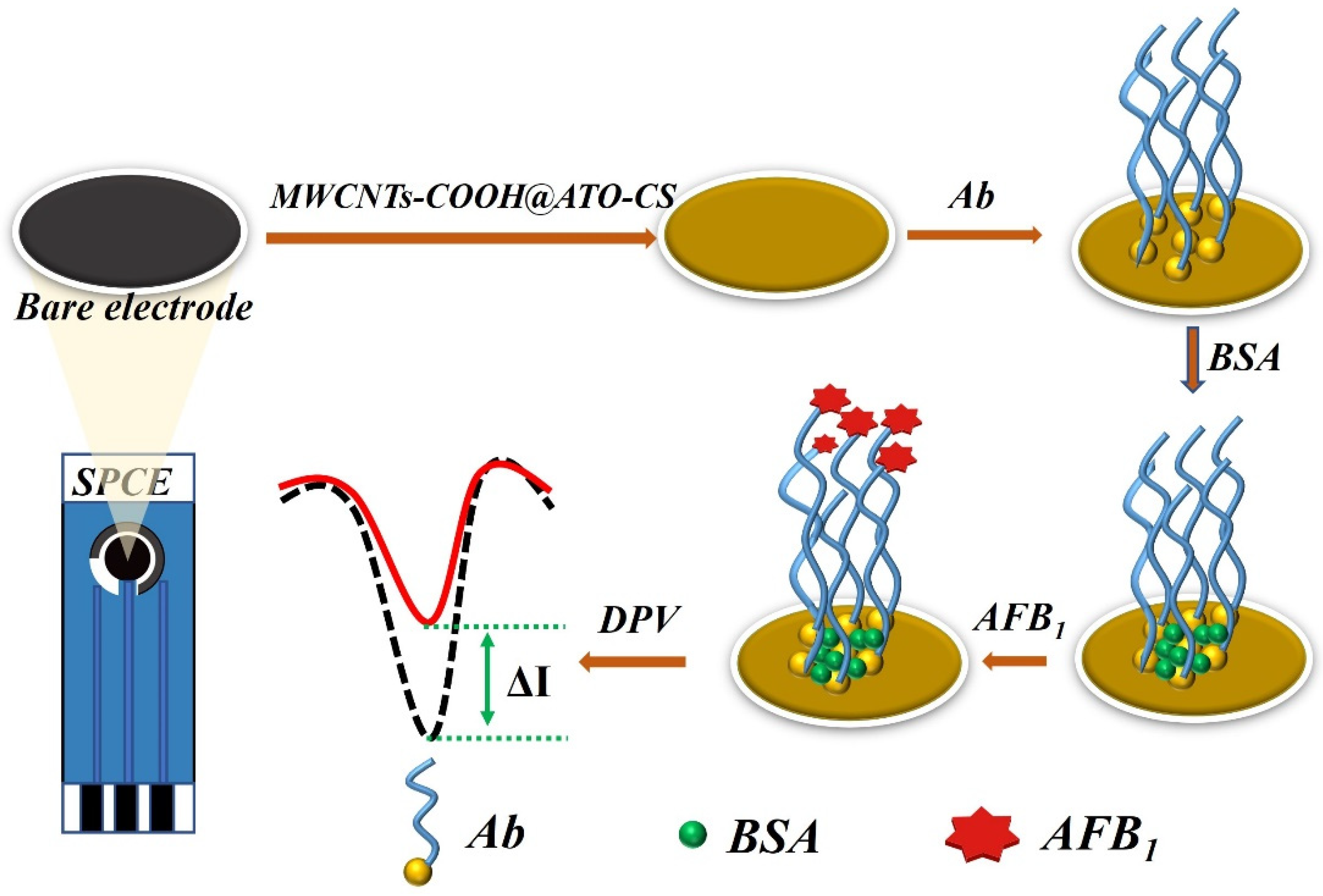
Micromachines, Free Full-Text

Scavenging of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species with

Micro Machines Play game online!

Micro Machines
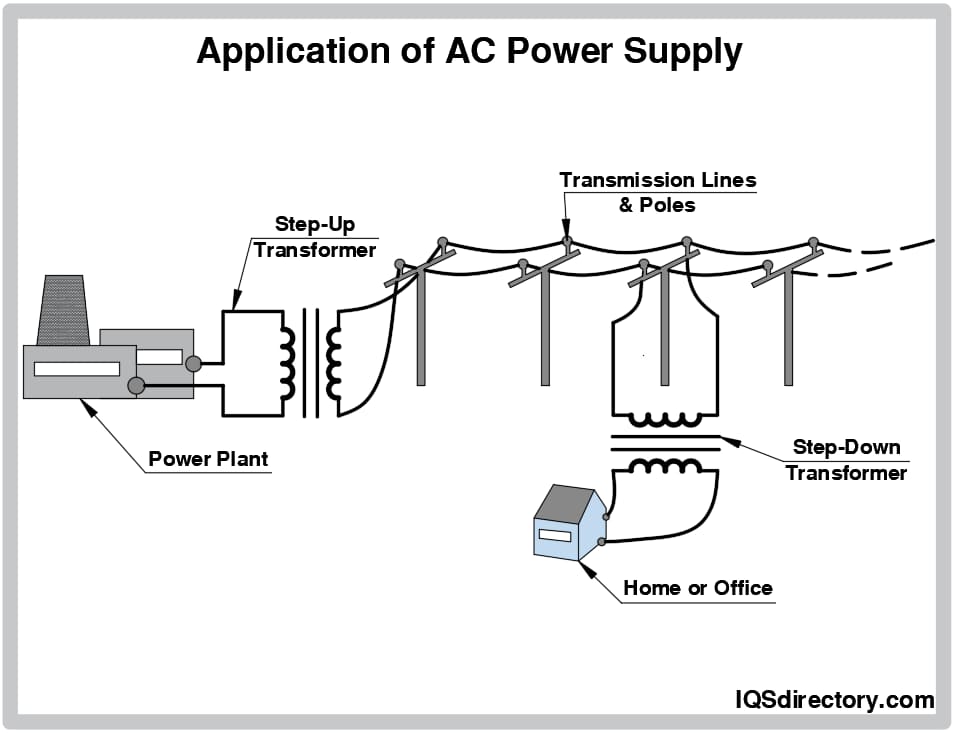
DC/DC Converters: Devices Capable of Converting to Higher or Lower

Micro Machines Super City Toolbox Action Playset, Jim Fong

2000 Micro Machines - JOE'S CURIOS

Micro Machines products for sale