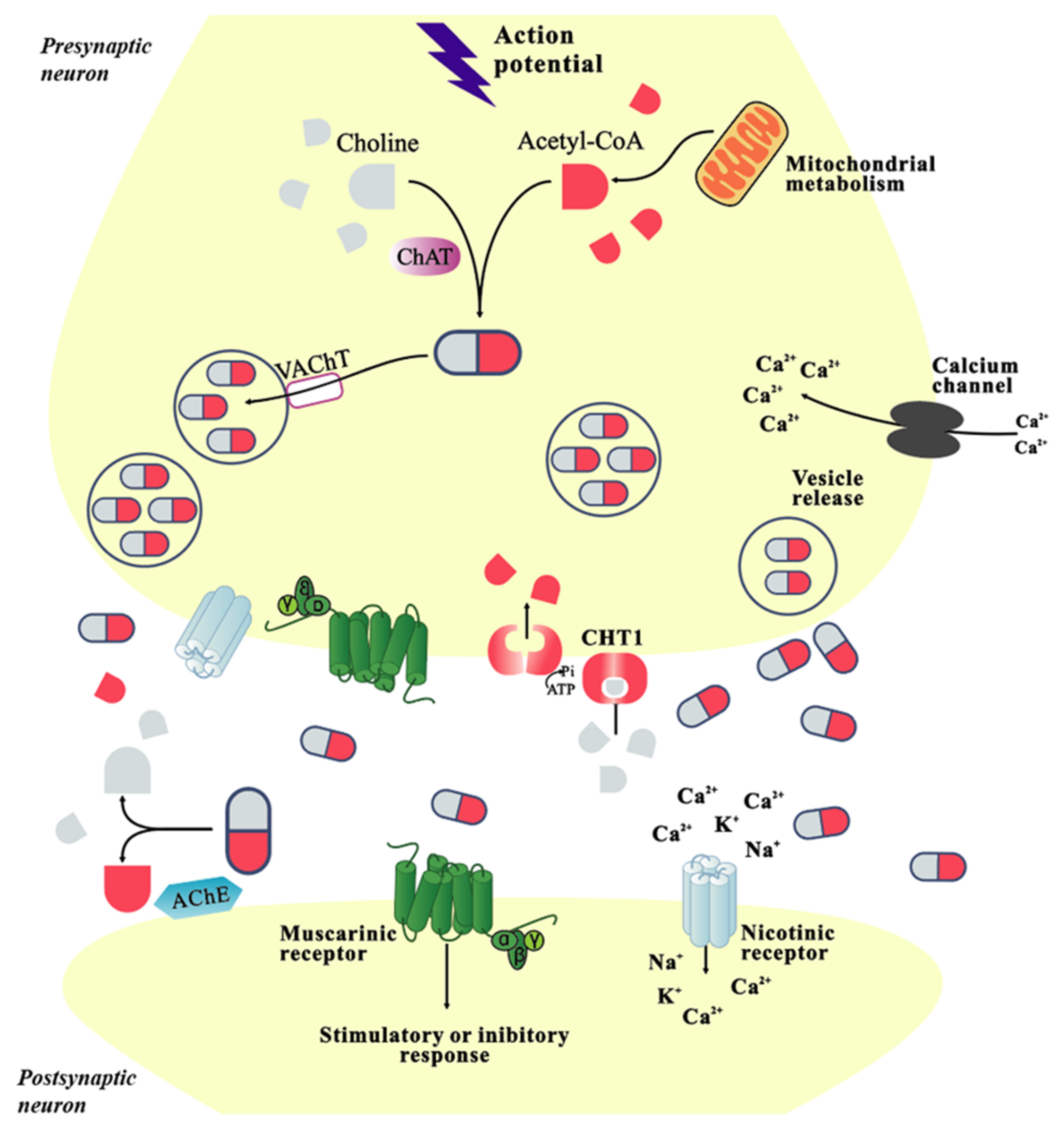
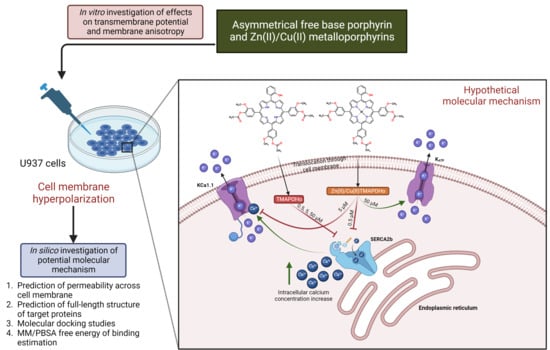
Acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter secreted by cholinergic neurons, is involved in signal transduction related to memory and learning ability. Alzheimer’s disease (AD), a progressive and commonly diagnosed neurodegenerative disease, is characterized by memory and cognitive decline and behavioral disorders. The pathogenesis of AD is complex and remains unclear, being affected by various factors. The cholinergic hypothesis is the earliest theory about the pathogenesis of AD. Cholinergic atrophy and cognitive decline are accelerated in age-related neurodegenerative diseases such as AD. In addition, abnormal central cholinergic changes can also induce abnormal phosphorylation of ttau protein, nerve cell inflammation, cell apoptosis, and other pathological phenomena, but the exact mechanism of action is still unclear. Due to the complex and unclear pathogenesis, effective methods to prevent and treat AD are unavailable, and research to explore novel therapeutic drugs is various and active in the world. This review summaries the role of cholinergic signaling and the correlation between the cholinergic signaling pathway with other risk factors in AD and provides the latest research about the efficient therapeutic drugs and treatment of AD.
Molecules, Free Full-Text, kelly godoy coelho

Molecules, Free Full-Text, onoo 2
Molecules, Free Full-Text, palusa vg

Molecules An Open Access Journal from MDPI
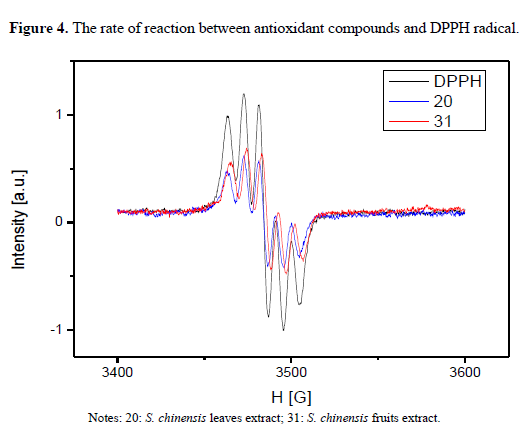
Molecules, Free Full-Text, Stearic Acid

Molecules, Free Full-Text, Stearic Acid
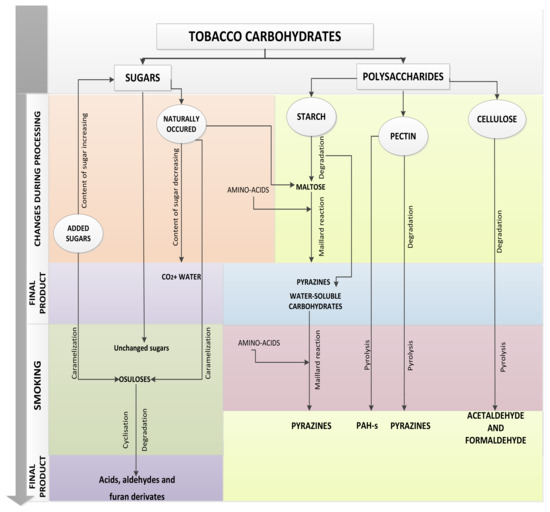
Molecules, Free Full-Text, players max cigarettes where to buy
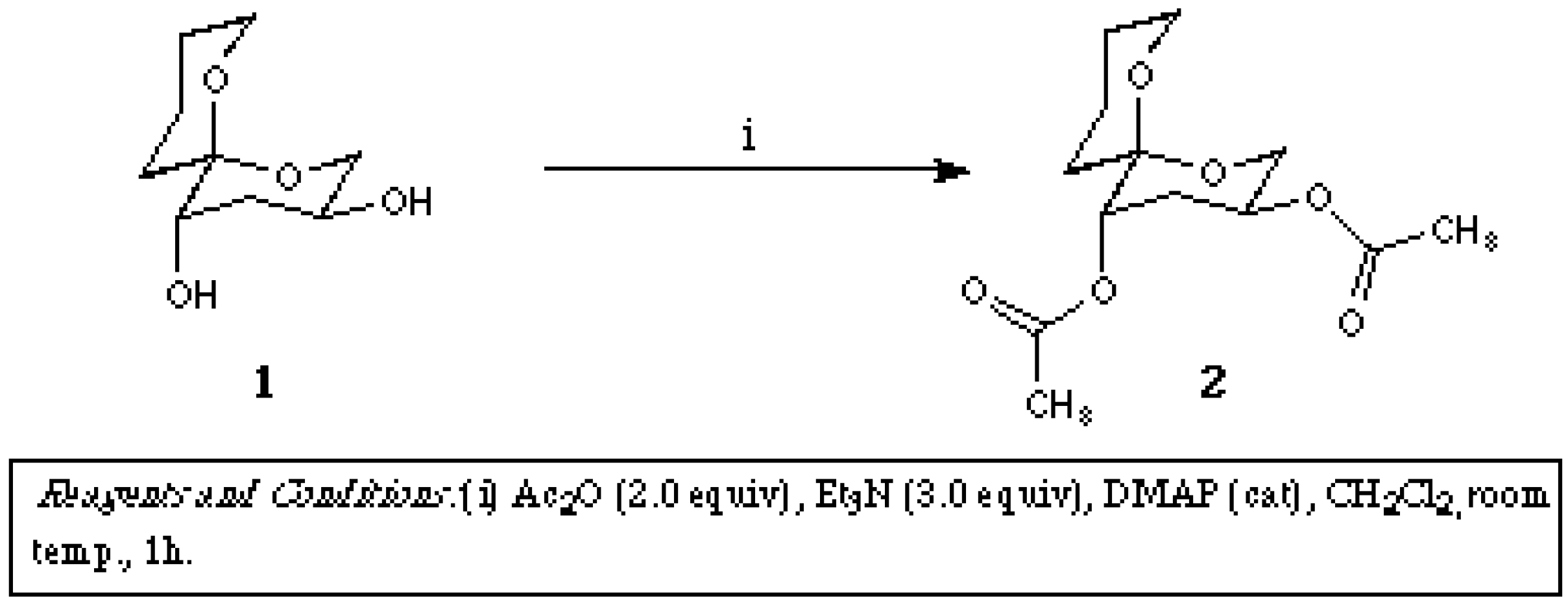
Molecules, Free Full-Text
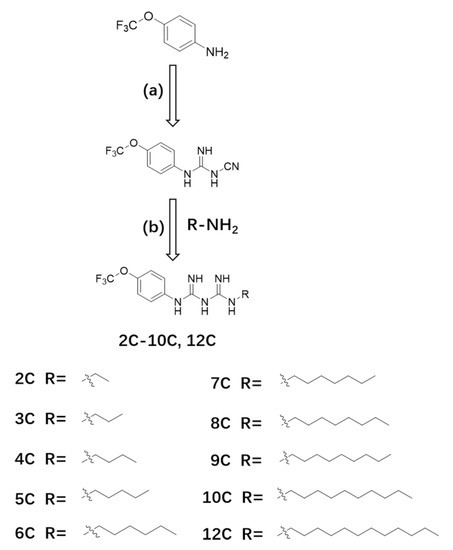
Molecules, Free Full-Text, chinese wall cpa 20
Molecules, Free Full-Text, players max cigarettes where to buy

Molecules, Free Full-Text, kelly godoy coelho

Molecules, Free Full-Text, kurnik dominó

Molecules, Free Full-Text, Stearic Acid
Molecules, Free Full-Text, mate pastor con negras

Molecules, Free Full-Text, Stearic Acid