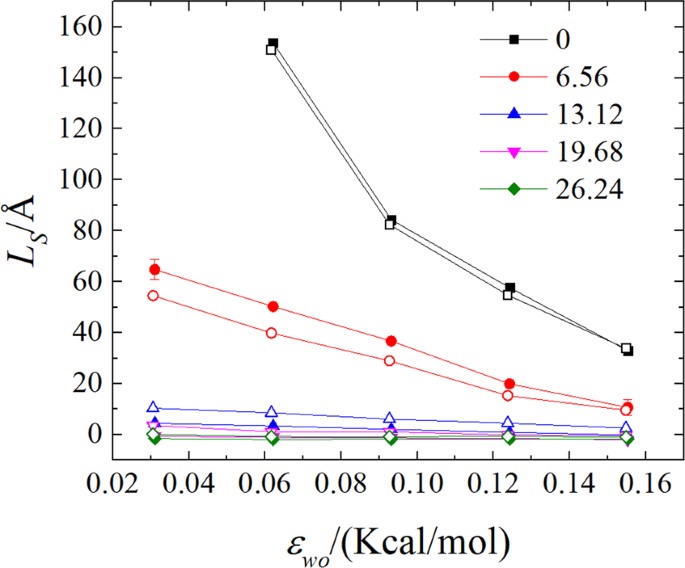
Slip length and structure of liquid water flowing past atomistic smooth charged walls
5 (295) · $ 27.50 · In stock
The influences of electric field intensity and driving force on the slip behaviour of water flow in a nanochannel

A Model for Wall Slip Prediction of Confined n-Alkanes: Effect of Wall-Fluid Interaction Versus Fluid Resistance

Slip length measurement in rectangular graphene nanochannels with a 3D flow analysis - ScienceDirect

9-3 Detecting the Quantum Fluctuation of Water
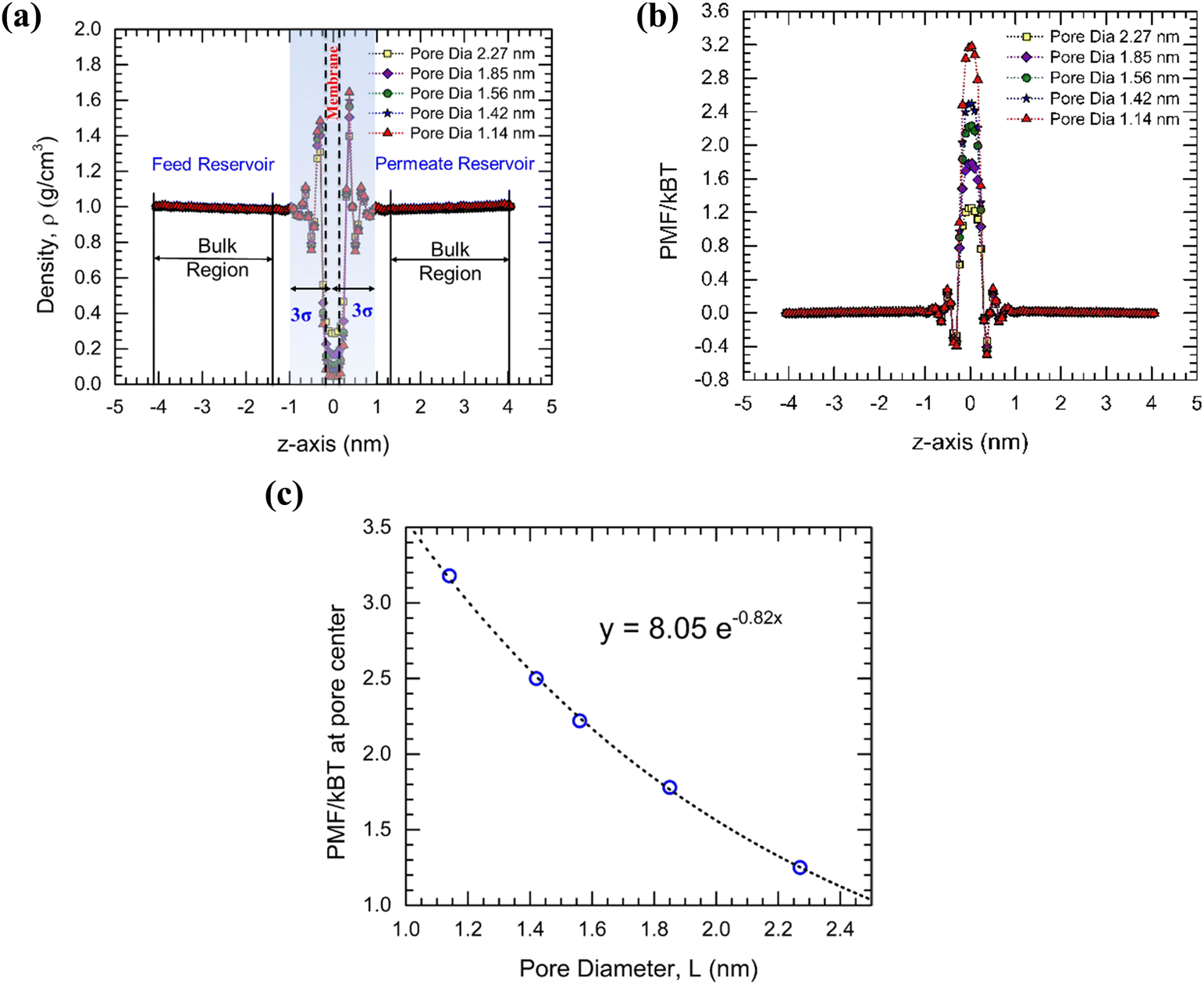
The validity of the continuum modeling limit in a single pore flows to the molecular scale - Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics (RSC Publishing) DOI:10.1039/D3CP02488A

Scaling law governing the roughness of the swash edge line

Extending the Classical Continuum Theory to Describe Water Flow through Two-Dimensional Nanopores

Properties of Water, Structure, Density & Molecules - Lesson

Viscosity ratios and slip length variations with the surface charge.

Comparisons of the velocity profiles between the MD simulation results
Thermo-osmotic flow in slit channels with boundary slip: giant flow amplification between polarized graphene surfaces, Journal of Fluid Mechanics

Slip length and structure of liquid water flowing past atomistic smooth charged walls
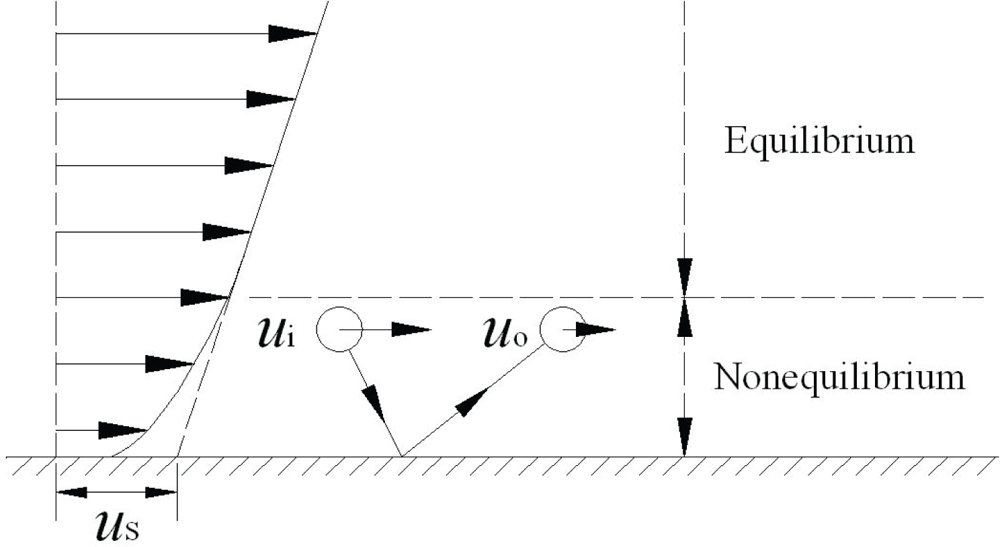
IJMS, Free Full-Text

Properties of Water from Numerical and Experimental Perspectives 0367138026, 9780367138028