Ultrasonography. - ppt download
4.9 (162) · $ 8.99 · In stock
Ultrasonography Ultrasound in the frequency range of 1 − 20 MHz is used in diagnostic ultrasonography. The velocity of propagation of ultrasound through a medium depends upon its compressibility. Lower compressibility results in higher velocity. Typical velocities in human tissues: 330 m/s in air (the lungs); 1, 540 m/s in soft tissue; and 3, 300 m/s in bone.
The velocity of propagation of ultrasound through a medium depends upon its compressibility. Lower compressibility results in higher velocity. Typical velocities in human tissues: 330 m/s in air (the lungs); 1, 540 m/s in soft tissue; and. 3, 300 m/s in bone.
Most modes of diagnostic ultrasonography are based upon the reflection of ultrasound at tissue interfaces. A gel is used to minimize the presence of air between the transducer and the skin to avoid reflection at the skin surface.
Large, smooth surfaces in a body cause specular reflection, whereas rough surfaces and regions cause nonspecular reflection or diffuse scatter.
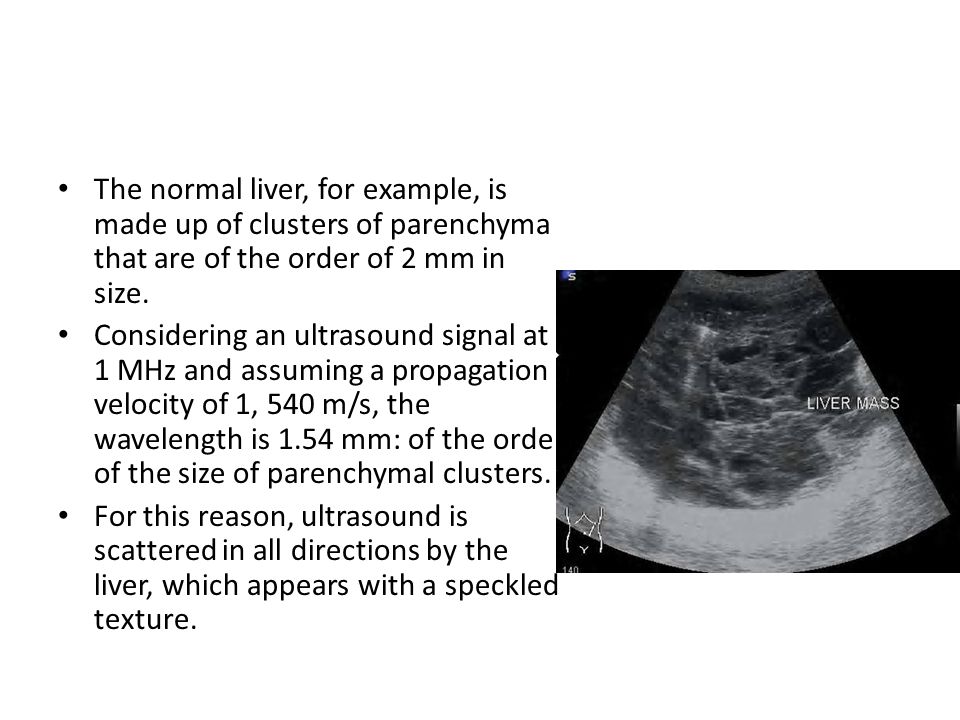
Considering an ultrasound signal at 1 MHz and assuming a propagation velocity of 1, 540 m/s, the wavelength is 1.54 mm: of the order of the size of parenchymal clusters. For this reason, ultrasound is scattered in all directions by the liver, which appears with a speckled texture.
tissues past bones and dense objects along the path of propagation of the beam are not imaged accurately.
Fluid-filled regions such as cysts have no internal structure, generate no echoes except at their boundaries, and appear as black regions on ultrasound images.
multiple reflections, speckle noise due to scattering, and. spatial distortion due to refraction. Spatial resolution of ultrasound images: 0.5 − 3 mm.
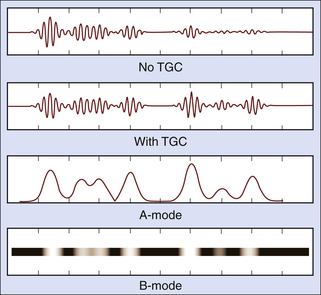
The amplitude (A) of the echoes is displayed on the vertical axis, with the corresponding depth (related to the time of arrival of the echo) on the horizontal axis. The A mode is useful in distance measurement (ranging), with applications in the detection of retinal detachment and the detection of shift of the midline of the brain.
The M mode is useful in the study of movement or motion (M), with applications in cardiac valve motion analysis.
An image of a 2D section or slice of the body is produced by using a single transducer to scan the region of interest or by using an array of sequentially activated transducers. Real-time imaging is possible at 15 − 40 fps. The B mode is useful in studying large organs, such as the liver, and in fetal imaging.
Useful in imaging blood flow. Detection of turbulence and retrograde flow: useful in the diagnosis of stenosis or insufficiency of cardiac valves and plaques in blood vessels. Doppler imaging may be used to obtain a combination of anatomic information with Bmode imaging and flow information obtained using pulsed Doppler.
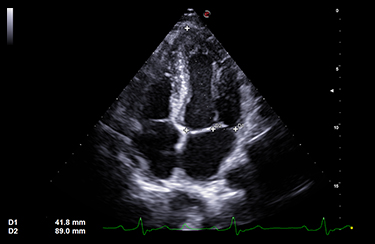
Mitral Valve (valve between left atrium and left ventricle)
– transrectal probes for imaging the prostate, – endovaginal probes for fetal imaging, – transesophageal probes for imaging the heart via the esophagus, and. – intravascular probes for the study of blood vessels.
An array of ultrasound transducers is used in the B mode to obtain a video illustrating the opening and closing activities of the valve leaflets. Useful in the detection of stenosis and loss of flexibility of the cardiac valves due to calcification.
The horizontal axis represents time. The echo signature of the mitral valve leaflets as they open and close is illustrated..
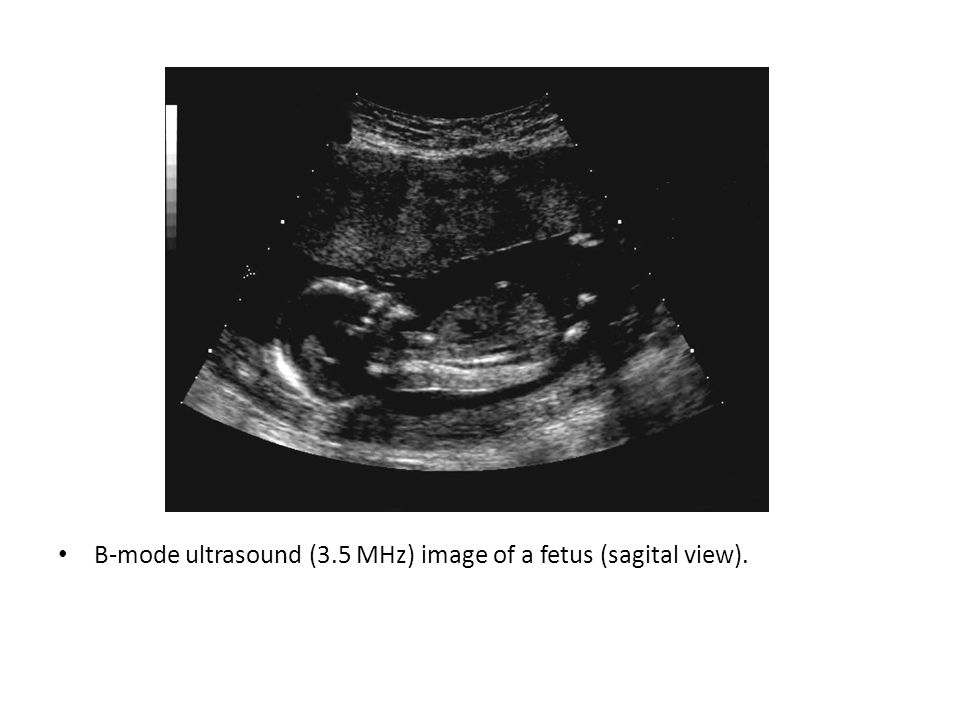
B-mode ultrasound (3.5 MHz) image of a fetus (sagital view).
Ultrasonography is particularly useful in fetal imaging. Ultrasonography is also useful in. tomographic imaging, discriminating between solid masses and fluid filled cysts in the breast, and. tissue characterization.
Mumps PowerPoint Template

Ultrasonography

Understanding Vascular Ultrasonography - ppt download

About Ultrasonography - ppt download

Breast ultrasound

Technology For Diagnostic Sonography Ppt Powerpoint Presentation

Basics of Ultrasound

OPTHALMIC ULTRASONOGRAPHY - ppt download
ACUTE ABDOMEN systemic sonographic approach to acute abdomen in emergency department: a case series, The Ultrasound Journal

ACUTE ABDOMEN systemic sonographic approach to acute abdomen in emergency department: a case series, The Ultrasound Journal

Ultrasonography. - ppt download

Breast ultrasound
Ultrasonography. - ppt download

Dr. Bill Parker discusses pre-op imaging for #fibroids 📣 Always