Guillain-Barré and Alpha-gal Syndromes: Saccharides-induced Immune Responses
4.7 (700) · $ 24.50 · In stock
The molecular interactions between hosts, vectors and pathogens drive the etiology of infectious diseases. At first sight, the Guillain-Barré and Alpha-Gal syndromes have quite different etiologies but, as proposed here, a closer look into the immune response to galactose-containing oligosaccharide structures that characterizes these two diseases reveals striking commonalities. In this Opinion paper, we address the main molecular drivers of two apparently unrelated diseases, and how the characterization of the immune response and immunological tolerance would advance the control and prevention of these diseases.
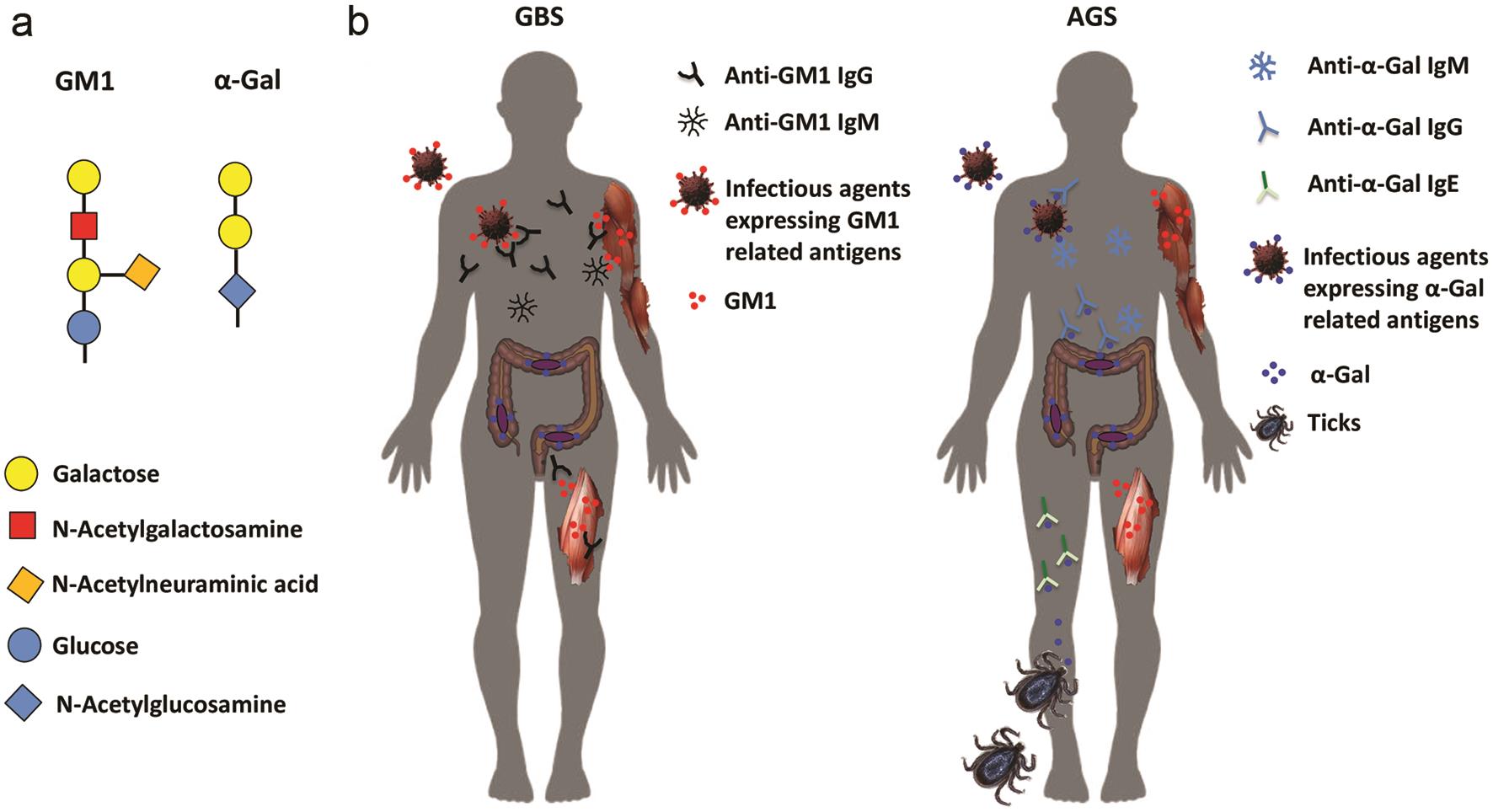
Guillain-Barré and Alpha-gal Syndromes: Saccharides-induced Immune Responses

Iván PACHECO, PhD Student, University of Castilla-La Mancha, Ciudad Real, Sanidad y Biotecnología (SaBio)
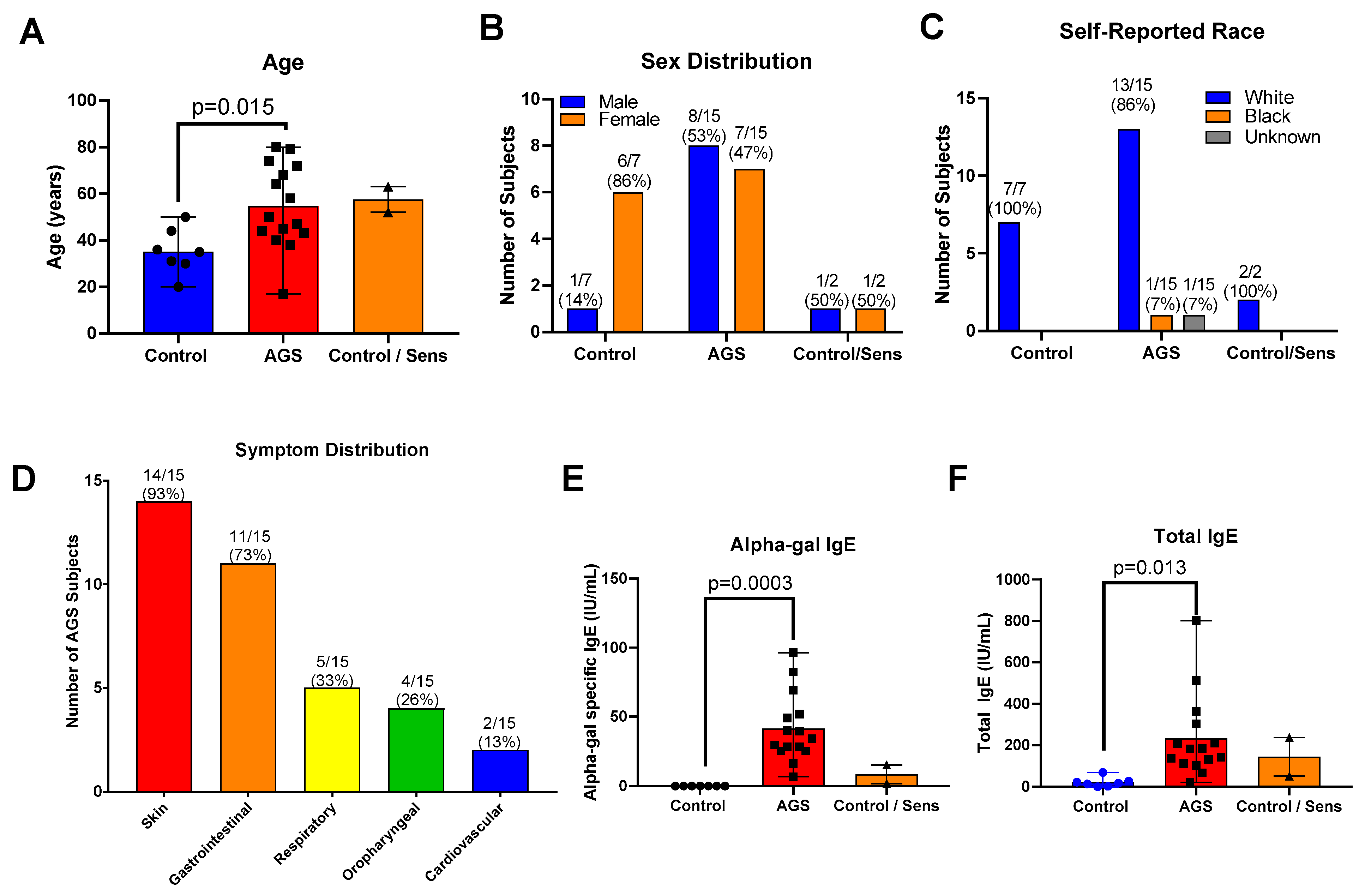
IJMS, Free Full-Text
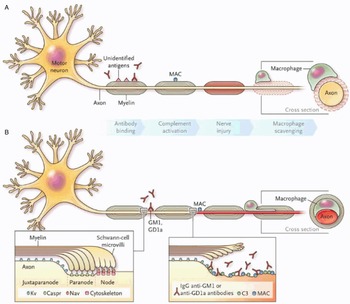
Guillain–Barré syndrome (Case 14) - Neuromuscular Disease
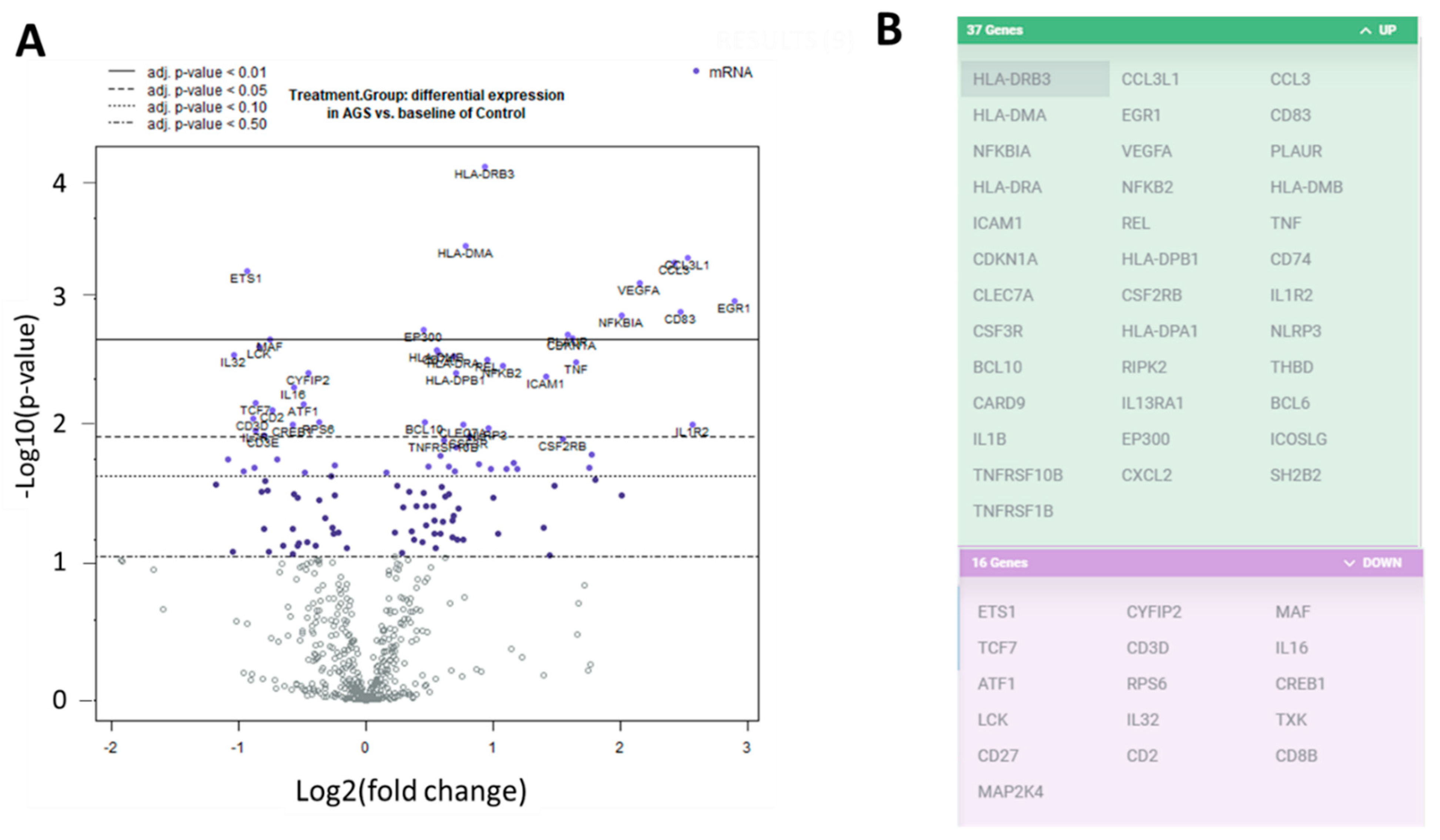
IJMS, Free Full-Text

Marinela CONTRERAS, PhD Juan de La Cierva Incorporación, PhD, Spanish National Research Council, Madrid, CSIC, Instituto de Investigación en Recursos Cinegéticos
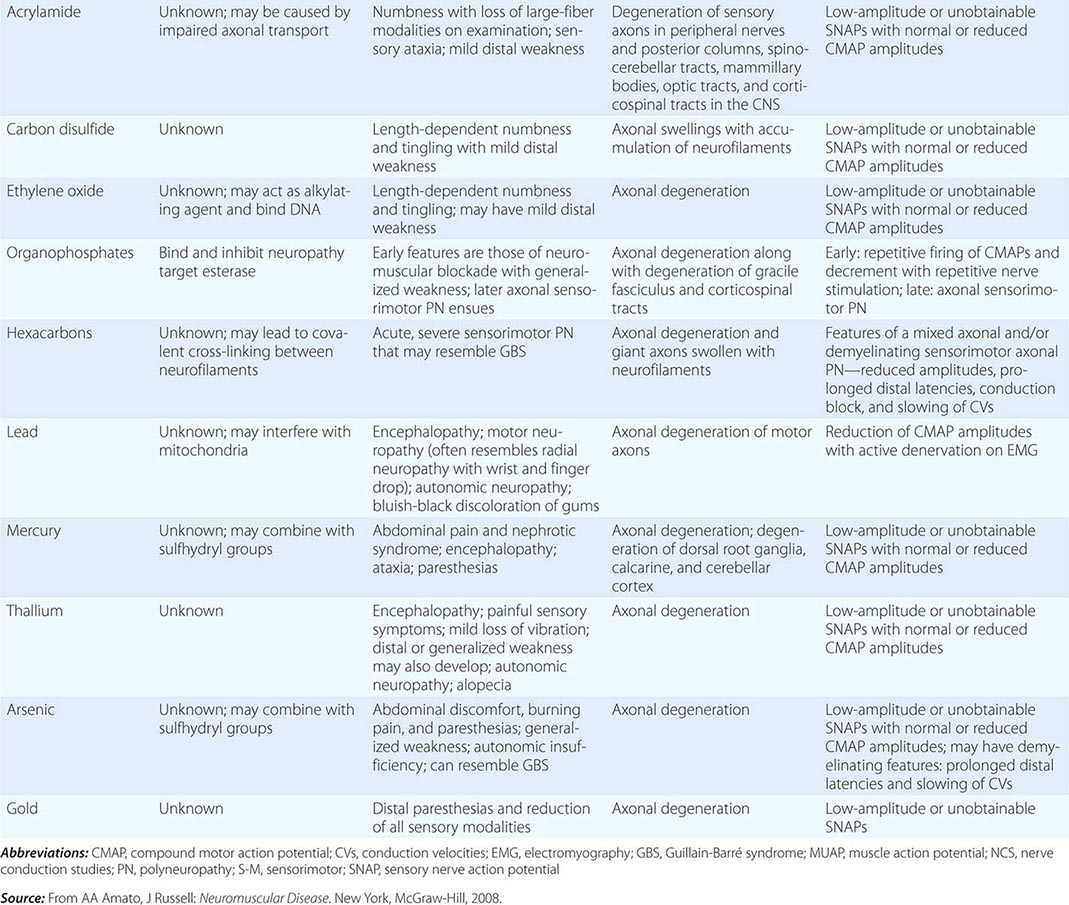
Guillain-Barré Syndrome and Other Immune-Mediated Neuropathies

Guillain–Barré syndrome in Asia Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery & Psychiatry

PDF) Quantitative proteomics reveals Piccolo as a candidate serological correlate of recovery from Guillain-Barr? syndrome

Guillain-Barré syndrome and anti-ganglioside antibodies: a clinician-scientist's journey. - Abstract - Europe PMC

Full article: Intestinal mucin-type O-glycans: the major players in the host-bacteria-rotavirus interactions

Publications Database - Alpha-gal Information