The myeloproliferative blood cancers—essential thrombocytosis (ET)
4.5 (660) · $ 13.50 · In stock
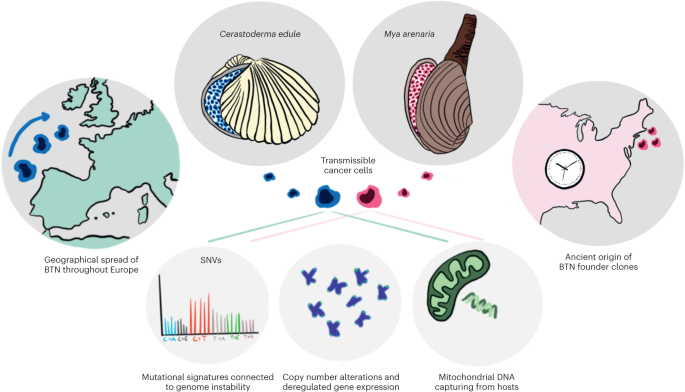
Download scientific diagram | The myeloproliferative blood cancers—essential thrombocytosis (ET), polycythemia vera (PV), and myelofibrosis (MF)—(MPNs) evolve in a biological continuum, spanning 5-10-20 years from the early cancer stages (ET/PV) towards the advanced MF stage. Chronic inflammation is the driving force for this development giving rise to increasing oxidative stress and increasing genomic instability. Inflammatory cytokines drive clonal evolution, and the clone itself generates oxidative stress and inflammatory products which in a self-perpetuating vicious circle elicits more fuel to the fire. In the initial stages of MPNs (ET, PV, and hyperproliferative MF), blood cell counts are elevated (in PV always red blood cells but very often leukocytes and platelets as well, in ET always elevated platelet counts and in some patients elevated leukocyte counts as well and in MF elevated leukocyte and platelet counts). Neuroinflammation is associated with several chronic inflammatory diseases. It is argued that chronic systemic inflammation in MPNs may also elicit neuroinflammation in MPNs and contribute to the CNS-symptom burden in patients with MPNs. It is hypothesized that MPNs are “A Human Neuroinflammation Model” for Alzheimer’s disease development from publication: Myeloproliferative blood cancers as a human neuroinflammation model for development of Alzheimer's disease: Evidences and perspectives | Chronic inflammation and involvement of myeloid blood cells are associated with the development of Alzheimer's disease (AD). Chronic inflammation is a highly important driving force for the development and progression of the chronic myeloproliferative blood cancers (MPNs), | Hematological Malignancies, Hydroxyurea and Essential Thrombocythemia | ResearchGate, the professional network for scientists.

Blood and Hematology - Essential Thrombocythemia Thrombocytosis (platelet count ≥450,000 per cubic millimeter) is frequently encountered in clinical practice, with a reported prevalence of 1.9% in a large study involving ambulatory patients
Essential Thrombocythemia - 1.

Myeloproliferative Neoplasms Leukemia and Lymphoma Society

Lasse Kjær's research works Zealand University Hospital, Køge

Essential Thrombocythemia Infographic – MPN Research Foundation
Pathology Outlines - Essential thrombocythemia

American Journal of Hematology, Blood Research Journal

Thrombosis in myeloproliferative neoplasms during cytoreductive and antithrombotic drug treatment - Research and Practice in Thrombosis and Haemostasis
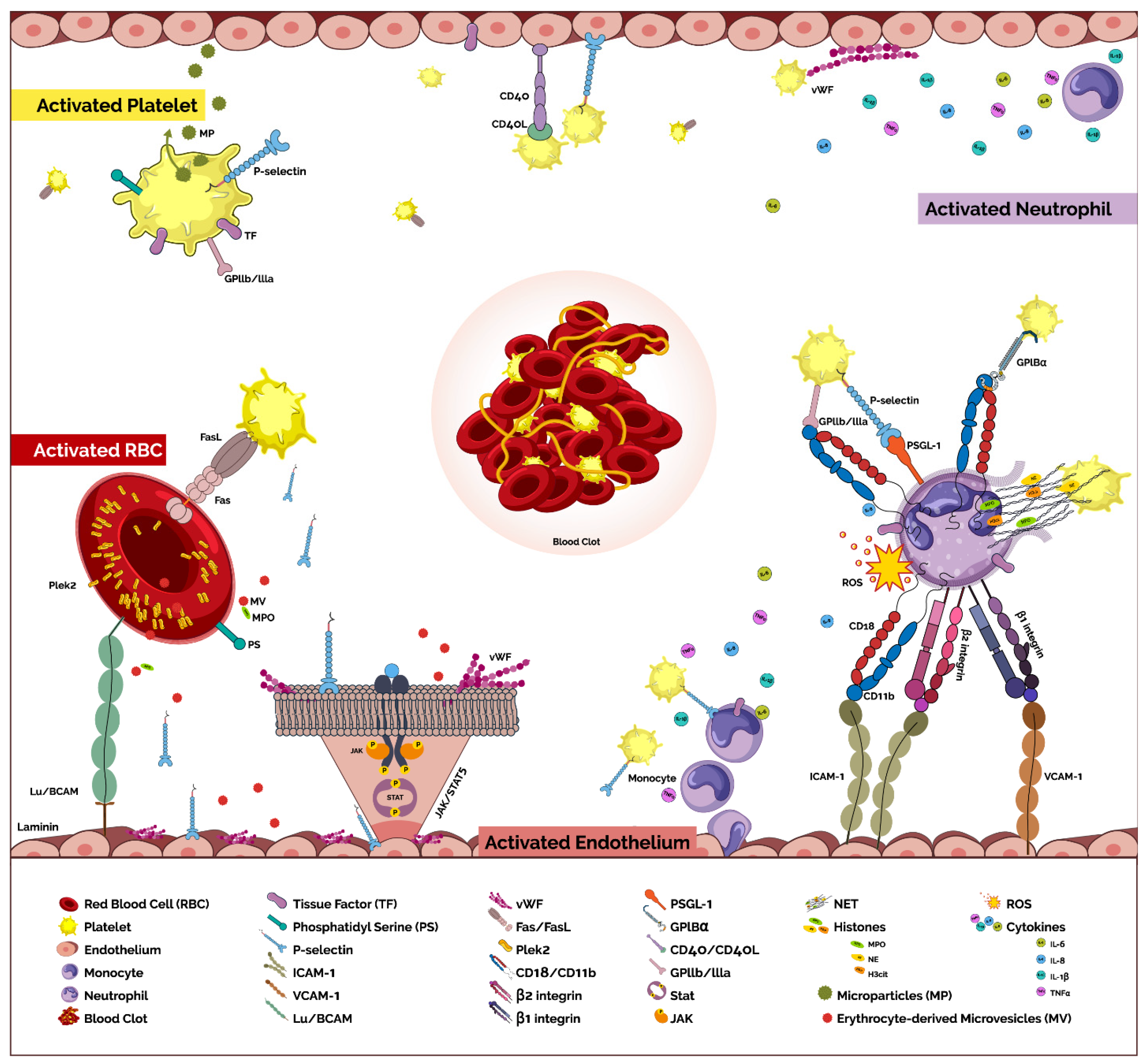
Hemato, Free Full-Text

What Causes Essential Thrombocythemia?