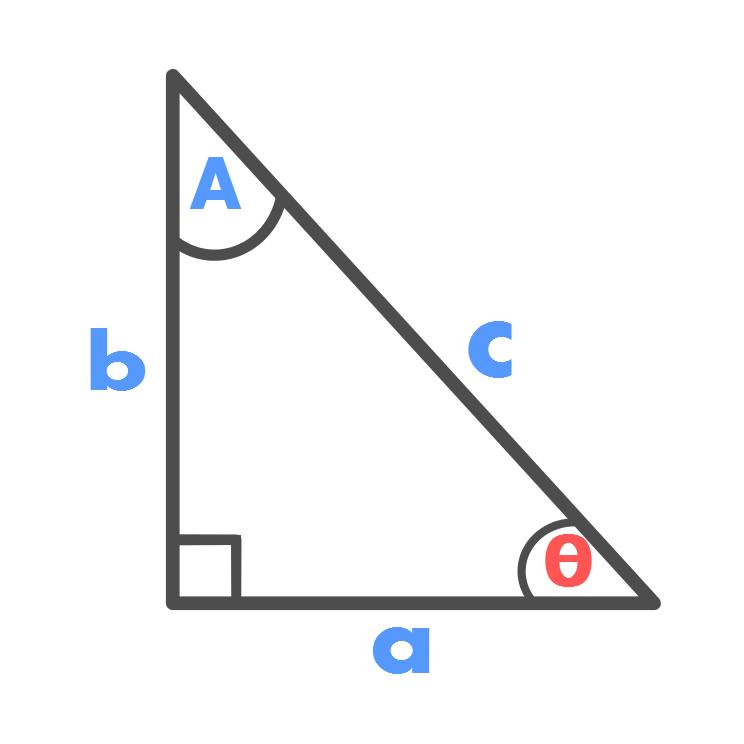
Midpoint Theorem on Right-angled Triangle, Proof, Statement
4.7 (746) · $ 10.99 · In stock
Here we will prove that in a right-angled triangle the median drawn to the hypotenuse is half the hypotenuse in length. Solution: In ∆PQR, ∠Q = 90°. QD is the median drawn to hypotenuse PR

MidPoint Theorem: Learn Statement, Proof, Converse, with Examples

Midpoint Theorem - Statement, Proof, Converse, Examples
What is the proof of midpoint theorem? - Quora
What is the proof of midpoint theorem? - Quora
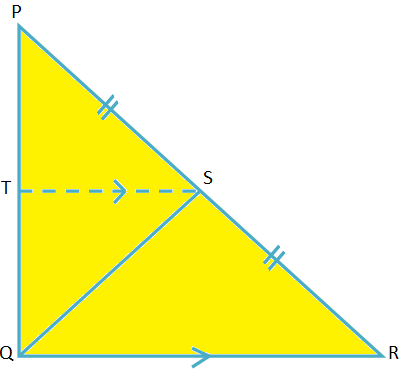
Midpoint Theorem on Right-angled Triangle, Proof, Statement

Prove that in a right angled triangle, the line segment joining the midpoint of the hypotenuse to the opposite vertex is half the hypotenuse.

Assignment 4 Write-Up

SOLVED: Triangle ABC is a right triangle. Point D is the midpoint of side AB, and point E is the midpoint of side AC. The measure of angle ADE is 36°. The
In a right triangle, prove that the line segment joining the mid point of the hypotenuse to the opposite vertex is half of the hypotenuse

Completing Proofs Involving Congruent Triangles Using ASA or AAS Practice, Geometry Practice Problems
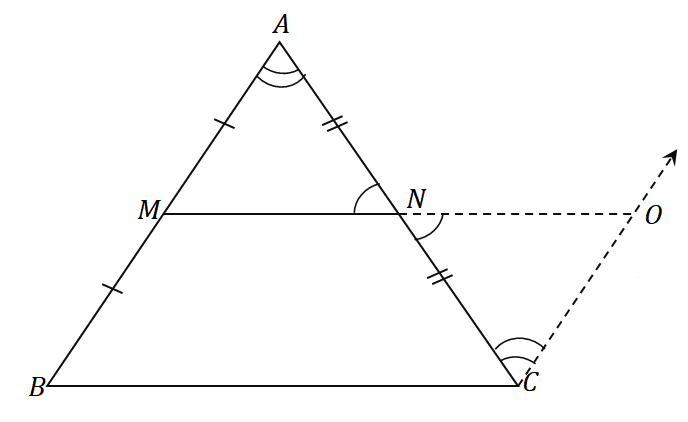
Midpoint Theorem - Conditions, Formula, and Applications - The Story of Mathematics - A History of Mathematical Thought from Ancient Times to the Modern Day
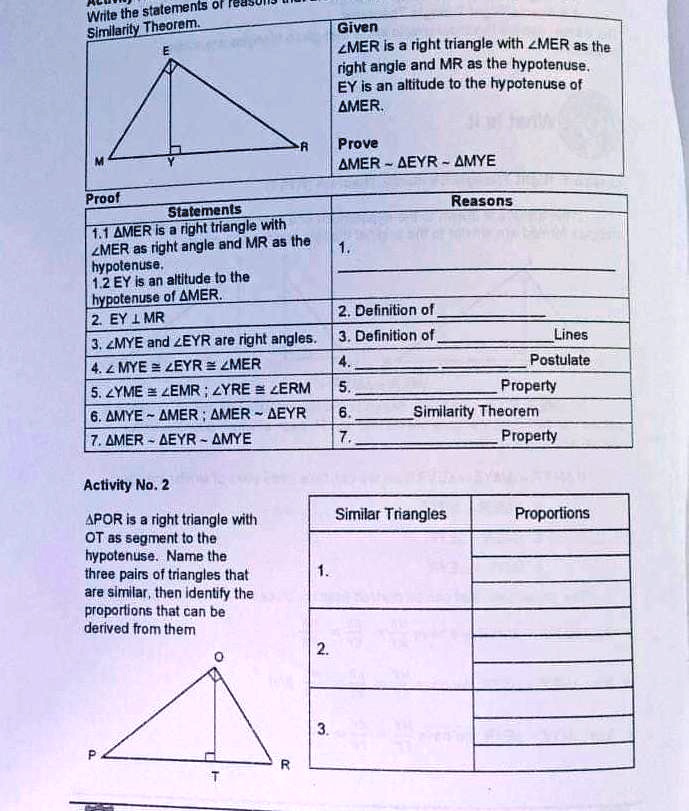
SOLVED: Statements: 1. Given LMER is a right triangle with ZMER as the right angle and MR as the hypotenuse. 2. EY is an altitude to the hypotenuse of AMER. Prove: AMER
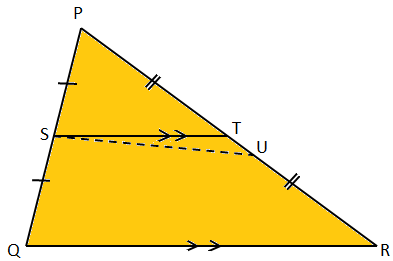
Converse of Midpoint Theorem Proof of Converse of Midpoint Theorem

Solved Given: • Point S is the midpoint of AQ • Point S is