Therapeutic application of regeneration-associated cells: a novel
4.5 (317) · $ 19.99 · In stock
Chronic diseases with comorbidities or associated risk factors may impair the function of regenerative cells and the regenerative microenvironment. Following this consideration, the vasculogenic conditioning culture (VCC) method was developed to boost the regenerative microenvironment to achieve regeneration-associated cells (RACs), which contain vasculogenic endothelial progenitor cells (EPCs) and anti-inflammatory/anti-immunity cells. Preclinical and clinical studies demonstrate that RAC transplantation is a safe and convenient cell population for promoting ischemic tissue recovery based on its strong vasculogenicity and functionality. The outputs of the scientific reports reviewed in the present study shed light on the fact that RAC transplantation is efficient in curing various diseases. Here, we compactly highlight the universal features of RACs and the latest progress in their translation toward clinics.

Cell therapy trials for heart regeneration — lessons learned and

Vasculogenic Conditioning of Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells

Human peripheral blood mononuclear cells enriched in endothelial

Stem-cell associated cell surface marker expression was observed

Effect of Repetitive Intra-Arterial Infusion of Bone Marrow

Interleukin-10 Deficiency Impairs Reparative Properties of Bone

QQ culture conditioning increased definitive EPC-CFU in vitro. (A

Therapeutic application of regeneration-associated cells: a novel

PDF) Therapeutic application of regeneration-associated cells: a

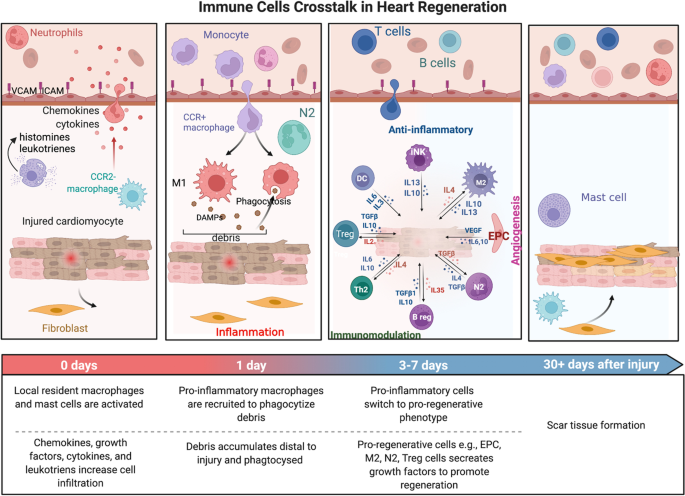
Schematic representation of the mechanisms underlying the

QQc restores tubular formation of diabetic progenitor cells. A

Monocyte and macrophage heterogeneity in the heart. - Abstract

Endothelial PGC-1α mediates vascular dysfunction in diabetes