- Home
- postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome
- Proteomic analysis reveals sex-specific biomarker signature in postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome, BMC Cardiovascular Disorders
Proteomic analysis reveals sex-specific biomarker signature in postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome, BMC Cardiovascular Disorders
4.5 (404) · $ 5.50 · In stock
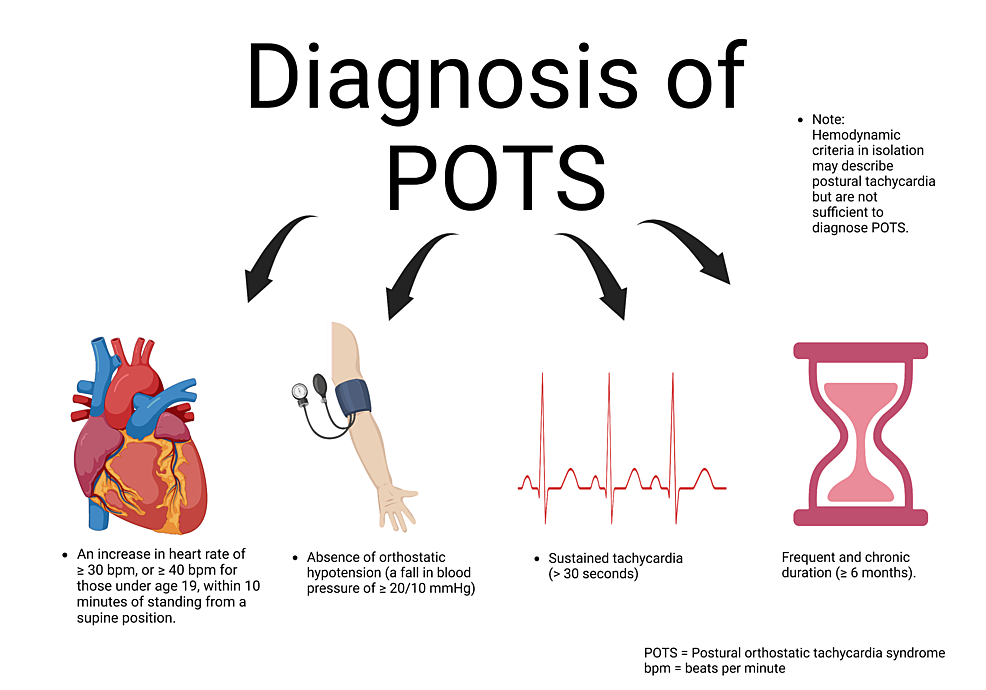
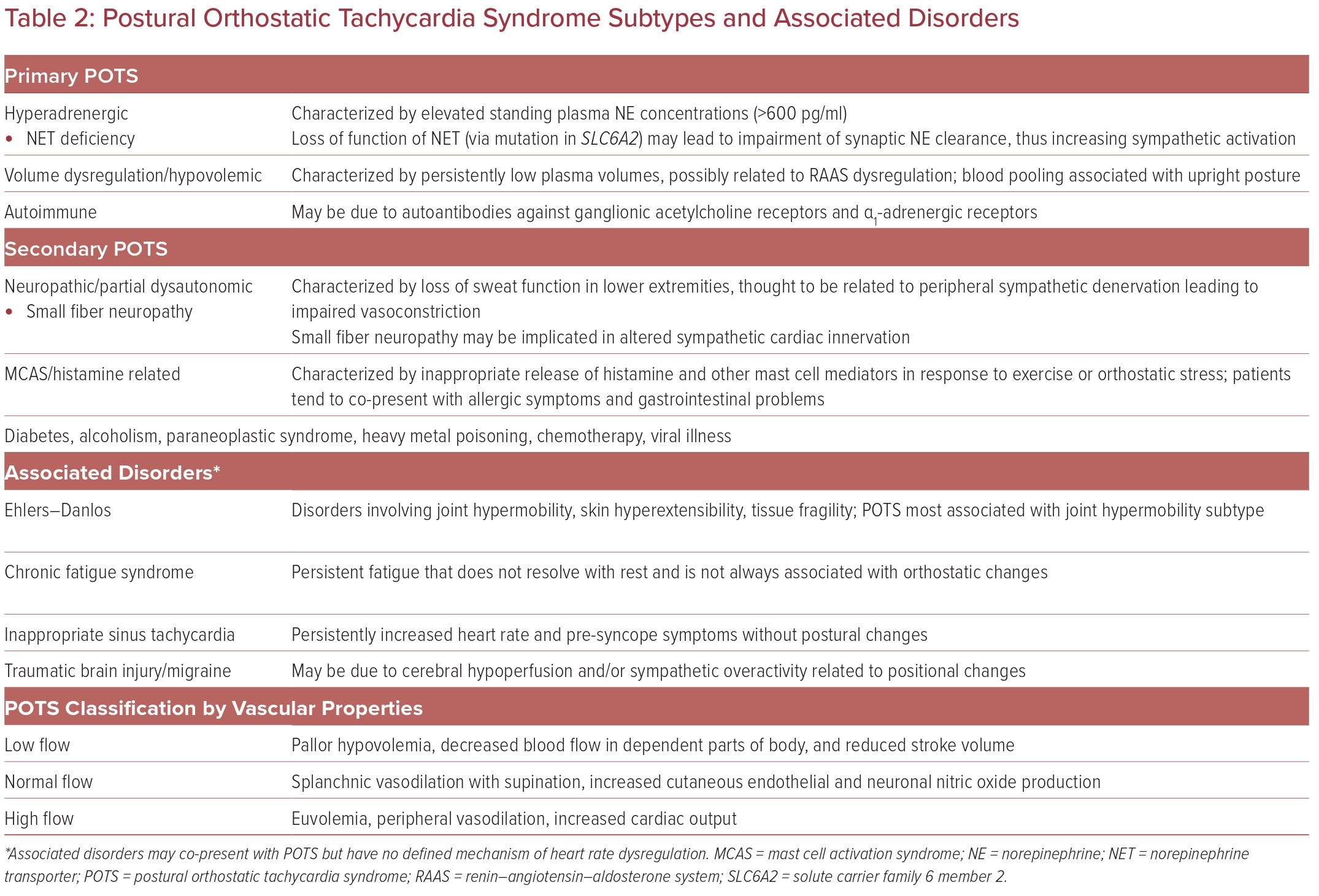
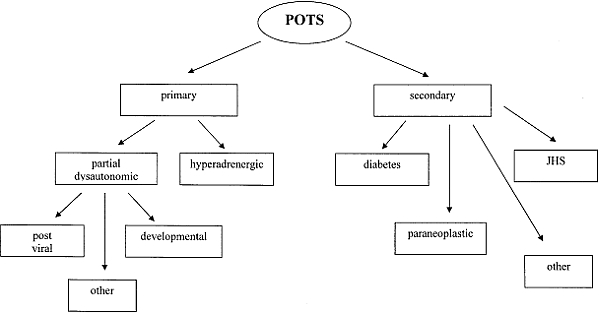
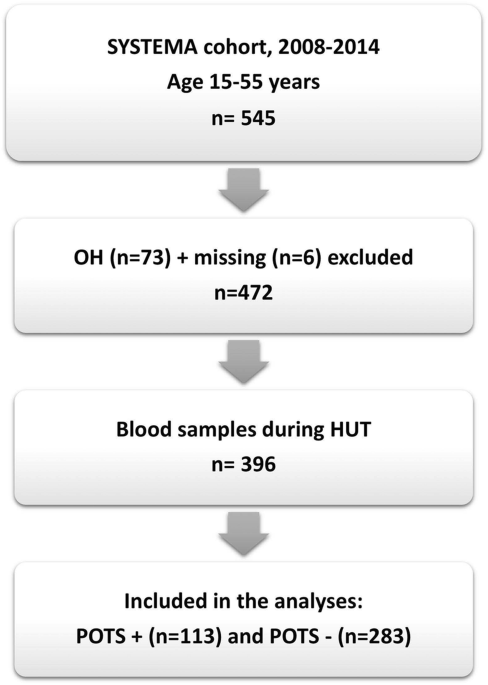
Background Postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome (POTS) is a variant of cardiovascular (CV) autonomic disorder of unknown etiology characterized by an excessive heart rate increase on standing and orthostatic intolerance. In this study we sought to identify novel CV biomarkers potentially implicated in POTS pathophysiology. Methods We conducted a nested case-control study within the Syncope Study of Unselected Population in Malmö (SYSTEMA) cohort including 396 patients (age range, 15–50 years) with either POTS (n = 113) or normal hemodynamic response during passive head-up-tilt test (n = 283). We used a targeted approach to explore changes in cardiovascular proteomics associated with POTS through a sequential two-stage process including supervised principal component analysis and univariate ANOVA with Bonferroni correction. Results POTS patients were younger (26 vs. 31 years; p < 0.001) and had lower BMI than controls. The discovery algorithm identified growth hormone (GH) and myoglobin (MB) as the most specific biomarker fingerprint for POTS. Plasma level of GH was higher (9.37 vs 8.37 of normalised protein expression units (NPX); p = 0.002), whereas MB was lower (4.86 vs 5.14 NPX; p = 0.002) in POTS compared with controls. In multivariate regression analysis, adjusted for age and BMI, and stratified by sex, lower MB level in men and higher GH level in women remained independently associated with POTS. Conclusions Cardiovascular proteomics analysis revealed sex-specific biomarker signature in POTS featured by higher plasma level of GH in women and lower plasma level of MB in men. These findings point to sex-specific immune-neuroendocrine dysregulation and deconditioning as potentially key pathophysiological traits underlying POTS.
Plasma proteomic profiling in postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome ( POTS) reveals new disease pathways

Proteomic Signatures of Lifestyle Risk Factors for Cardiovascular Disease: A Cross‐Sectional Analysis of the Plasma Proteome in the Framingham Heart Study

43rd International Symposium on Intensive Care & Emergency Medicine, Critical Care

Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome Is Associated With Elevated G‐Protein Coupled Receptor Autoantibodies

Small molecule metabolites: discovery of biomarkers and therapeutic targets. - Abstract - Europe PMC

Baroreflex control of muscle sympathetic nerve activity in postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome

Proteomic analysis reveals sex-specific biomarker signature in postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome, BMC Cardiovascular Disorders

Dr. Artur Fedorowski Publications

Proteomic analysis of cardiometabolic biomarkers and predictive modeling of severe outcomes in patients hospitalized with COVID-19, Cardiovascular Diabetology

Ultrarare Variants in DNA Damage Repair Genes in Pediatric Acute-Onset Neuropsychiatric Syndrome or Acute Behavioral Regression in Neurodevelopmental Disorders
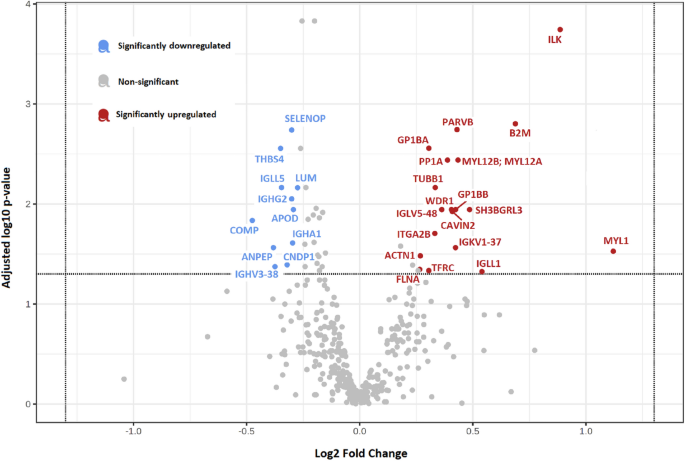
Plasma proteomic profiling in postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome ( POTS) reveals new disease pathways

Quantitative proteomic analysis of human serum using tandem mass tags to predict cardiovascular risks in patients with psoriasis

iBright Imaging System Resources