Intermittent pneumatic compression therapy (IPC). The extremity to
4.9 (267) · $ 27.99 · In stock
Download scientific diagram | Intermittent pneumatic compression therapy (IPC). The extremity to be treated is placed in the (still) deflated cuff (a). An electronic control device (b) is used to adjust the pressure gradient, treatment intervals, and overall treatment duration, resulting in intermittent inflation of the twelve-chamber cuffs (c). from publication: Compression therapy in patients with venous leg ulcers | Wund‐D.A.CH. is the umbrella organization of the various wound care societies in German‐speaking countries. The present consensus paper on practical aspects pertinent to compression therapy in patients with venous leg ulcers was developed by experts from Germany, Austria, and | Leg Ulcer, Compression and Intermittent Pneumatic Compression Devices | ResearchGate, the professional network for scientists.

Intermittent Pneumatic Compression Therapy –(IPCT) Mohammed TA, Omar Ph.D. PT, PGDCR Rehabilitation Health Science Department-CAMS-KSU. - ppt download

Quality medical pneumatic compression Designed For Varied Uses
FeaturesSEQUENTIAL COMPRESSION THERAPYImproves circulation and blood flow to provide pain relief. Excellent for rehabilitation and pre or post
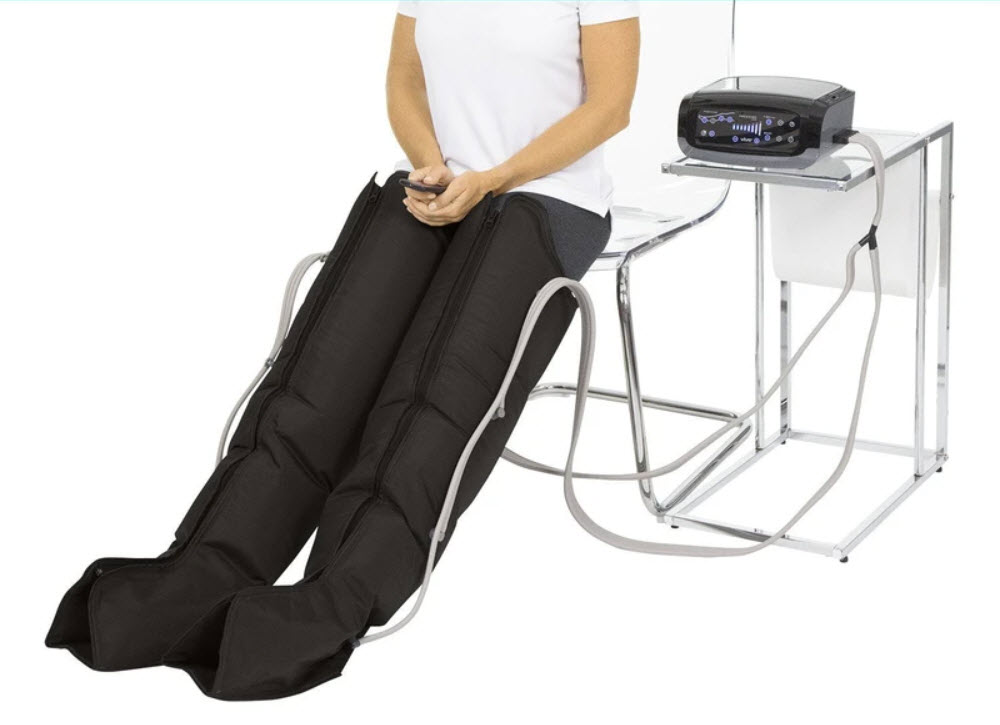
Sequential Compression Device - Leg Sleeves and Pump by Vive Health
The effect of intermittent pneumatic compression on leg pain, with a

PDF] Intermittent pneumatic compression therapy: a systematic review.
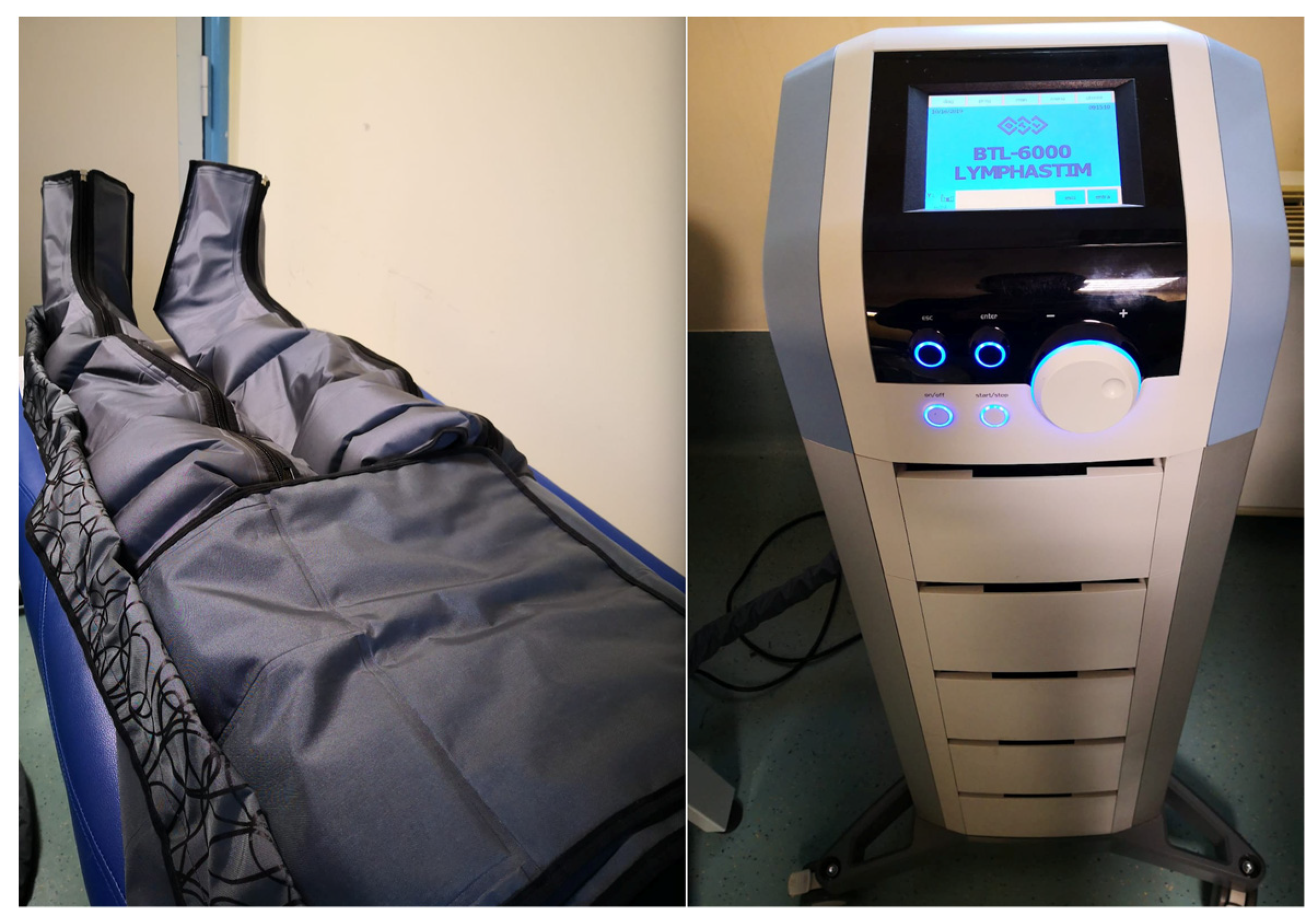
Medicina, Free Full-Text
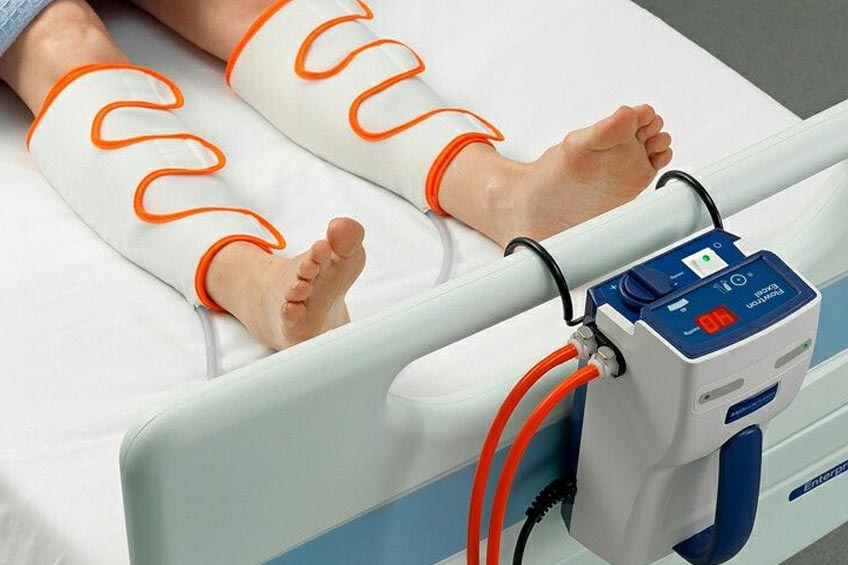
Portable DVT Pumps Manufacturers in Ghaziabad, Best Portable DVT Pumps Suppliers Exporters Ghaziabad

Highly Advanced intermittent pneumatic compression therapy
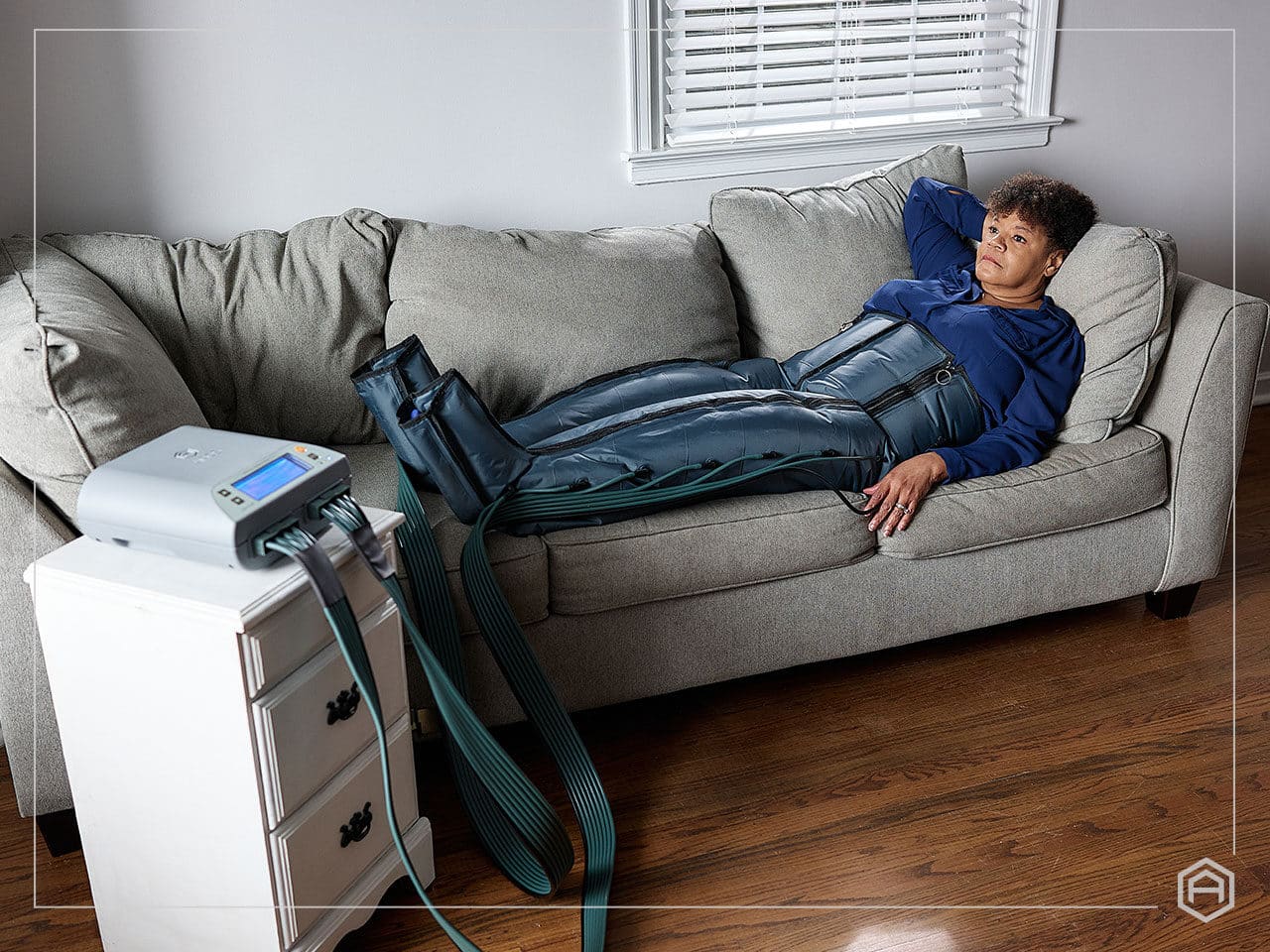
Intermittent pneumatic compression pump therapy for lymphedema •

MLD and IPC Archives - Lympha Press®
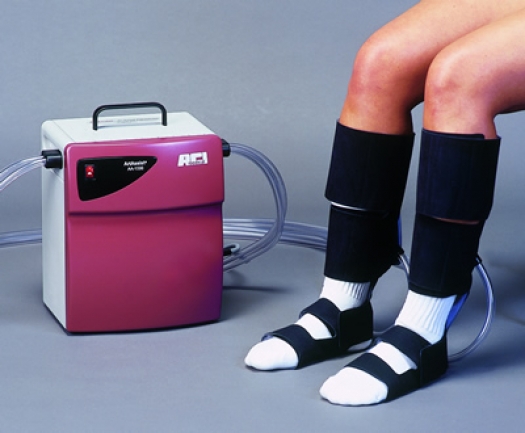
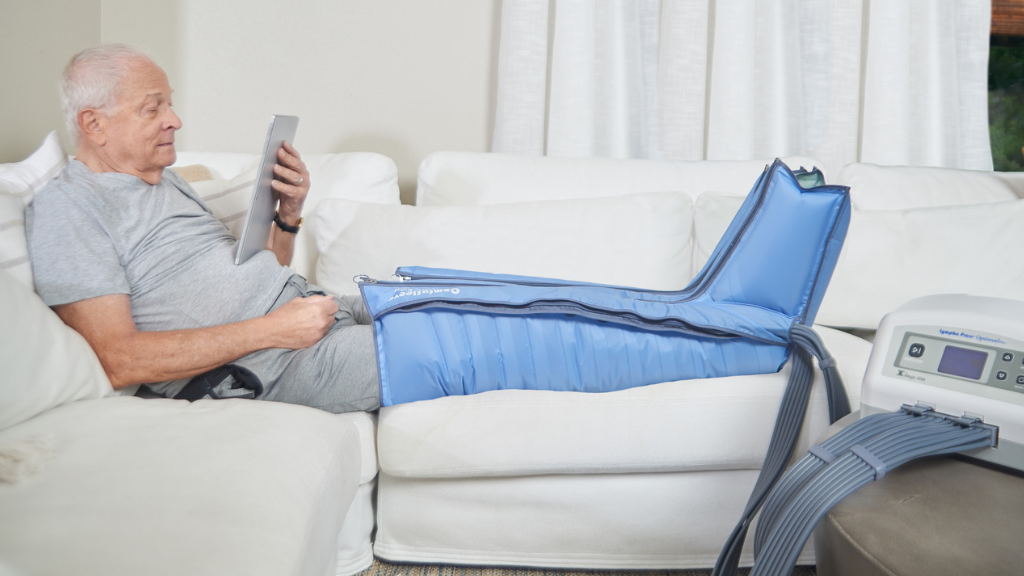
Using a Pneumatic Compression Device for Lower and Upper Extremity Peripheral Arterial Disease
Intermittent Pneumatic Compression (IPC) Therapy - CoreNewport

Quality intermittent pneumatic compression devices Designed For Varied Uses

PDF] Intermittent pneumatic compression therapy: a systematic review.